Quality and resource efficiency in hospital service provision: A geoadditive stochastic frontier analysis of stroke quality of care in Germany
- PMID: 30188906
- PMCID: PMC6126832
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203017
Quality and resource efficiency in hospital service provision: A geoadditive stochastic frontier analysis of stroke quality of care in Germany
Abstract
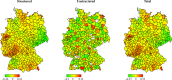
We specify a Bayesian, geoadditive Stochastic Frontier Analysis (SFA) model to assess hospital performance along the dimensions of resources and quality of stroke care in German hospitals. With 1,100 annual observations and data from 2006 to 2013 and risk-adjusted patient volume as output, we introduce a production function that captures quality, resource inputs, hospital inefficiency determinants and spatial patterns of inefficiencies. With high relevance for hospital management and health system regulators, we identify performance improvement mechanisms by considering marginal effects for the average hospital. Specialization and certification can substantially reduce mortality. Regional and hospital-level concentration can improve quality and resource efficiency. Finally, our results demonstrate a trade-off between quality improvement and resource reduction and substantial regional variation in efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Street A, Gutacker N, Bojke C, Devlin N, Daidone S. Variations in outcome and costs among NHS providers for common surgical procedures: econometric analyses of routinely collected data. Health Services and Delivery Research. 2014;(21). - PubMed
-
- OECD. Focus on Health Spending. OECD Health Statistics. 2015;.
-
- Grieco PLE, McDevitt RC. Productivity and Quality in Health Care: Evidence from the Dialysis Industry. The Review of Economic Studies. 2016; p. forthcoming. 10.1093/restud/rdw042 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical