Global gray matter morphometry differences between children with reading disability, ADHD, and comorbid reading disability/ADHD
- PMID: 30189332
- PMCID: PMC6940023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandl.2018.08.004
Global gray matter morphometry differences between children with reading disability, ADHD, and comorbid reading disability/ADHD
Abstract
Extensive, yet disparate, research exists elucidating structural anomalies in individuals with Reading Disability (RD) or ADHD. Despite ADHD and RD being highly comorbid, minimal research has attempted to determine shared patterns of morphometry between these disorders. In addition, there is no published research examining the morphometry of comorbid RD and ADHD (RD/ADHD). Hence, we conducted voxel-based morphometry on the MRI scans of 106 children, ages 8-12 years, with RD, ADHD, or RD/ADHD, and typically developing controls. We found right caudate and superior frontal regions in both RD and ADHD, along with areas specific to RD and to ADHD that are consistent with current theories on these disorders. Perhaps most importantly, we found a potential neurobiological substrate for RD/ADHD. Further, our findings illustrate both shared and specific contributors to RD/ADHD, supporting two current theories on the comorbidity of RD and ADHD, thereby facilitating future work on potential etiologies of RD/ADHD.
Keywords: ADHD; Frontal lobes; Morphometry; Occipital lobes; Reading disability; Reading disability/ADHD; Striatum; Structural neuroimaging; Thalamus; VBM.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
None.
Figures
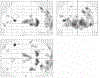

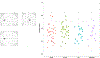
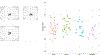
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- Ashburner J (2010). VBM Tutorial, 1–14.
-
- Baddeley AD, & Hitch GJ (1994). Developments in the concept of working memory. Neuropsychology, 8(4), 485–493. 10.1037/0894-4105.8.4.485. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

