Markers Involved in Innate Immunity and Neutrophil Activation are Elevated during Acute Human Anaphylaxis: Validation of a Microarray Study
- PMID: 30189430
- PMCID: PMC6738247
- DOI: 10.1159/000492301
Markers Involved in Innate Immunity and Neutrophil Activation are Elevated during Acute Human Anaphylaxis: Validation of a Microarray Study
Abstract
Background: We have previously identified the upregulation of the innate immune response, neutrophil activation, and apoptosis during anaphylaxis using a microarray approach. This study aimed to validate the differential gene expression and investigate protein concentrations of "hub genes" and upstream regulators during anaphylaxis.
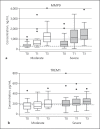
Methods: Samples were collected from patients with anaphylaxis on their arrival at the emergency department, and after 1 and 3 h. mRNA levels of 11 genes (interleukin-6 [IL-6], IL-10, oncostatin M [OSM], S100A8, S100A9, matrix metalloproteinase 9 [MMP9], FASL, toll-like receptor 4 [TLR4], MYD88, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 [TREM1], and cluster of differentiation 64 [CD64]) were measured in peripheral blood leucocytes using qPCR. Serum protein concentrations were measured by ELISA or cytometric bead array for 6 of these candidates.
Results: Of 69 anaphylaxis patients enrolled, 36 (52%) had severe reactions, and 38 (55%) were female. Increases in both mRNA and protein of IL-10, S100A9, MMP9, and TREM1 were observed. OSM, S100A8, TLR4, and CD64 were upregulated and IL-6 protein concentrations were increased during anaphylaxis. Both FASL and soluble Fas ligand decreased during anaphylaxis.
Conclusion: These results provide evidence for the involvement of innate immune pathways and myeloid cells during human anaphylaxis, validating previous microarray findings. Elevated S100A8, S100A9, TLR4, and TREM1 expression, and increased S100A9 and soluble TREM1 protein concentrations strongly suggest that neutrophils are activated during acute anaphylaxis.
Keywords: Allergy; Anaphylaxis; Myeloid cells; Neutrophils.
© 2018 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Poulos LM, Waters AM, Correll PK, Loblay RH, Marks GB. Trends in hospitalizations for anaphylaxis, angioedema, and urticaria in Australia, 1993–1994 to 2004–2005. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:878–884. - PubMed
-
- Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson Jr NF, Bock SA, Branum A, Brown SGA, Camargo Jr CA, Cydulka R, Galli SJ, Gidudu J, Gruchalla RS, Harlor Jr AD, Hepner DL, Lewis LM, Lieberman PL, Metcalfe DD, O'Connor R, Muraro A, Rudman A, Schmitt C, Scherrer D, Simons FER, Thomas S, Wood JP, Decker WW. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report-second national institute of allergy and infectious disease/food allergy and anaphylaxis network symposium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:391–397. - PubMed
-
- Simons FER. Anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125((2 suppl 2)):S161–S181. - PubMed
-
- Stone SF, Cotterell C, Isbister GK, Holdgate A, Brown SG. Elevated serum cytokines during human anaphylaxis: Identification of potential mediators of acute allergic reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:786–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

