Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Property of Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chitosan Halogenated Acetates
- PMID: 30189609
- PMCID: PMC6165101
- DOI: 10.3390/md16090315
Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Property of Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chitosan Halogenated Acetates
Abstract
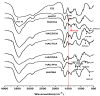
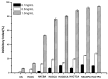
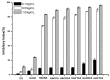
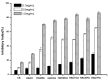
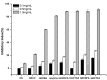
Hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan halogenated acetates were successfully synthesized from six different haloacetic acids and hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan (HACC) with high substitution degree, which are hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan bromacetate (HACBA), hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan chloroacetate (HACCA), hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan dichloroacetate (HACDCA), hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan trichloroacetate (HACTCA), hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan difluoroacetate (HACDFA), and hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan trifluoroacetate (HACTFA). These chitosan derivatives were synthesized by two steps: first, the hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan was synthesized by chitosan and 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride. Then, hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan halogenated acetates were synthesized via ion exchange. The structures of chitosan derivatives were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ¹H Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (¹H NMR), 13C Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (13C NMR), and elemental analysis. Their antifungal activities against Colletotrichum lagenarium, Fusarium graminearum, Botrytis cinerea, and Phomopsis asparagi were investigated by hypha measurement in vitro. The results revealed that hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan halogenated acetates had better antifungal activities than chitosan and HACC. In particular, the inhibitory activity decreased in the order: HACTFA > HACDFA > HACTCA > HACDCA > HACCA > HACBA > HACC > chitosan, which was consistent with the electron-withdrawing property of different halogenated acetates. This experiment provides a potential idea for the preparation of new antifungal drugs by chitosan.
Keywords: antifungal activity; electronegativity; halogenated acetate; hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Costa A.E.S., da Cunha F.S., Honorato A., Capucho A.S., Dias R., Borel J.C., Ishikawa F.H. Resistance to Fusarium Wilt in watermelon accessions inoculated by chlamydospores. Sci. Hortic. 2018;228:181–186. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.10.007. - DOI
-
- Garmendia G., Umpierrez-Failache M., Ward T.J., Vero S. Development of a PCR-RFLP method based on the transcription elongation factor 1-alpha gene to differentiate Fusarium graminearum from other species within the Fusarium graminearum species complex. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2018;70:28–32. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.08.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sevastos A., Kalampokis I.F., Panagiotopoulou A., Pelecanou M., Aliferis K.A. Implication of Fusarium graminearum primary metabolism in its resistance to benzimidazole fungicides as revealed by 1H NMR metabolomics. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2018;148:50–61. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.03.015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

