Actin-Myosin Interaction: Structure, Function and Drug Discovery
- PMID: 30189615
- PMCID: PMC6163256
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092628
Actin-Myosin Interaction: Structure, Function and Drug Discovery
Abstract
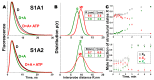
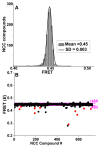
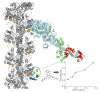
Actin-myosin interactions play crucial roles in the generation of cellular force and movement. The molecular mechanism involves structural transitions at the interface between actin and myosin's catalytic domain, and within myosin's light chain domain, which contains binding sites for essential (ELC) and regulatory light chains (RLC). High-resolution crystal structures of isolated actin and myosin, along with cryo-electron micrographs of actin-myosin complexes, have been used to construct detailed structural models for actin-myosin interactions. However, these methods are limited by disorder, particularly within the light chain domain, and they do not capture the dynamics within this complex under physiological conditions in solution. Here we highlight the contributions of site-directed fluorescent probes and time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) in understanding the structural dynamics of the actin-myosin complex in solution. A donor fluorescent probe on actin and an acceptor fluorescent probe on myosin, together with high performance TR-FRET, directly resolves structural states in the bound actin-myosin complex during its interaction with adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Results from these studies have profound implications for understanding the contractile function of actomyosin and establish the feasibility for the discovery of allosteric modulators of the actin-myosin interaction, with the ultimate goal of developing therapies for muscle disorders.
Keywords: ATP; FRET; actin; drug discovery; fluorescence; heart failure; myosin.
Conflict of interest statement
D.D.T. holds equity in, and serves as President of, Photonic Pharma LLC. This relationship has been reviewed and managed by the University of Minnesota. Photonic Pharma had no role in this study.
Figures



References
-
- Thomas D.D., Muretta J.M., Colson B.A., Mello R.N., Kast D. Spectroscopic Probes of Muscle Proteins. In: Edward H.E., editor. Comprehensive Biophysics. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2012. pp. 226–250.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

