Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 30189978
- PMCID: PMC6156553
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0557
Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
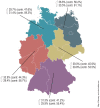
Background: Essential arterial hypertension is one of the main treatable cardiovascular risk factors. In Germany, approximately 13% of women and 18% of men have uncontrolled high blood pressure (≥ 140/90 mmHg).
Methods: This review is based on pertinent publications retrieved by a selective literature search in PubMed.
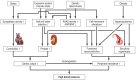
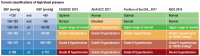
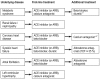
Results: Arterial hypertension is diagnosed when repeated measurements in a doctor's office yield values of 140/90 mmHg or higher. The diagnosis should be confirmed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring or by home measurement. Further risk factors and end-organ damage should be considered as well. According to the current European guidelines, the target blood pressure for all patients, including those with diabetes mellitus or renal failure, is <140/90 mmHg. If the treatment is well tolerated, further lowering of blood pressure, with a defined lower limit, is recommended for most patients. The main non-pharmacological measures against high blood pressure are reduction of salt in the diet, avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption, smoking cessation, a balanced diet, physical exercise, and weight loss. The first-line drugs for arterial hypertension include long-acting dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers, and thiazide-like diuretics. Mineralocorticoid-receptor blockers are effective in patients whose blood pressure cannot be brought into acceptable range with first-line drugs.
Conclusion: In most patients with essential hypertension, the blood pressure can be well controlled and the cardiovascular risk reduced through a combination of lifestyle interventions and first-line antihypertensive drugs.
Figures

Comment in
-
Gynecological Causes Should Not Be Forgotten.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 1;116(5):70. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0070a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30950386 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evidence-Based Blood Pressure Goals.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 1;116(5):70. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0070b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30950387 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Off to a Bad Start With Fixed Combinations.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 1;116(5):70-71. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0070c. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30950388 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Small Target Group.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 1;116(5):71. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0071a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30950389 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genetic Factors Should Be Considered.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 1;116(5):71. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0071b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30950390 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Potential Drug Interactions Forgotten.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 1;116(5):71-72. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0071c. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30950391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet. 2008;371:1513–1518. - PubMed
-
- Vangen-Lonne AM, Wilsgaard T, Johnsen SH, Lochen ML, Njolstad I, Mathiesen EB. Declining incidence of ischemic stroke: what is the impact of changing risk factors? The Tromso Study 1995 to 2012. Stroke. 2017;48:544–550. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Oliveria SA, Lapuerta P, McCarthy BD, L‘Italien GJ, Berlowitz DR, Asch SM. Physician-related barriers to the effective management of uncontrolled hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:413–420. - PubMed
-
- Ho PM, Magid DJ, Shetterly SM, et al. Importance of therapy intensification and medication nonadherence for blood pressure control in patients with coronary disease. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:271–276. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

