R-loop generation during transcription: Formation, processing and cellular outcomes
- PMID: 30190235
- PMCID: PMC6340742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.08.009
R-loop generation during transcription: Formation, processing and cellular outcomes
Abstract
R-loops are structures consisting of an RNA-DNA duplex and an unpaired DNA strand. They can form during transcription upon nascent RNA "threadback" invasion into the DNA duplex to displace the non-template strand. Although R-loops occur naturally in all kingdoms of life and serve regulatory roles, they are often deleterious and can cause genomic instability. Of particular importance are the disastrous consequences when replication forks or transcription complexes collide with R-loops. The appropriate processing of R-loops is essential to avoid a number of human neurodegenerative and other clinical disorders. We provide a perspective on mechanistic aspects of R-loop formation and their resolution learned from studies in model systems. This should contribute to improved understanding of R-loop biological functions and enable their practical applications. We propose the novel employment of artificially-generated stable R-loops to selectively inactivate tumor cells.
Keywords: DNA repair; Non-canonical DNA structures; R-loops; RNA-DNA hybrids; Transcription-replication collisions.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures
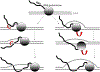


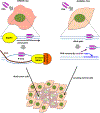
References
-
- Daube SS and von Hippel PH (1994) RNA displacement pathways during transcription from synthetic RNA-DNA bubble duplexes. Biochemistry, 33, 340347. - PubMed
-
- Yin YW and Steitz TA (2004) The structural mechanism of translocation and helicase activity in T7 RNA polymerase. Cell, 116, 393–404. - PubMed
-
- Jiang M, Ma N, Vassylyev DG and McAllister WT (2004) RNA displacement and resolution of the transcription bubble during transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Mol Cell, 15, 777–788. - PubMed
-
- Korzheva N and Mustaev A (2001) Transcription elongation complex: structure and function. Curr Opin Microbiol, 4, 119–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

