Anti-inflammation effects of 8-oxo-9-octadecenoic acid isolated from Undaria peterseniana in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage cells
- PMID: 30190667
- PMCID: PMC6123615
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2018-1422
Anti-inflammation effects of 8-oxo-9-octadecenoic acid isolated from Undaria peterseniana in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage cells
Abstract
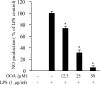
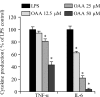
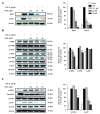
The aim of this study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory activity of 8-oxo-9-octadecenoic acid (OOA) isolated from Undaria peterseniana by examining its ability to inhibit the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. We found that OOA significantly suppressed the LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO) and inflammatory cytokines. OOA downregulated the LPS-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 proteins. With respect to proinflammatory signaling pathways, OOA inhibited LPS-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling by inhibiting the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). Moreover, OOA inhibited LPS-induced nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling by reducing the phosphorylation of IκB-α and p50 proteins. These results indicate that OOA significantly reduces proinflammatory signaling, which results in reduced expression of cytokines and proinflammatory mediators. Taken together, these results suggest that OOA has potent anti-inflammatory effects and could be considered an effective anti-inflammatory agent.
Keywords: 8-Oxo-9-octadecenoic acid; Undaria peterseniana; anti-inflammatory; lipopolysaccharide; macrophages.
Figures
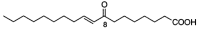
Similar articles
-
4-methoxycinnamyl p-coumarate isolated from Etlingera pavieana rhizomes inhibits inflammatory response via suppression of NF-κB, Akt and AP-1 signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.Phytomedicine. 2019 Feb 15;54:89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.193. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668386
-
Cnidilide, an alkylphthalide isolated from the roots of Cnidium officinale, suppresses LPS-induced NO, PGE2, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α production by AP-1 and NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27591413
-
Oryza sativa (Rice) Hull Extract Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW264.7 Macrophages by Suppressing Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase, c-Jun N-terminal Kinase, and Nuclear Factor-κB Activation.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 Oct-Dec;12(48):295-301. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.192198. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27867272 Free PMC article.
-
5-Bromo-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-benzaldehyde inhibited LPS-induced production of pro-inflammatory mediators through the inactivation of ERK, p38, and NF-κB pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Oct 25;258:108-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27569861
-
Zedoarondiol isolated from the rhizoma of Curcuma heyneana is involved in the inhibition of iNOS, COX-2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines via the downregulation of NF-kappaB pathway in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Aug;9(9):1049-57. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2009.04.012. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19398040
Cited by
-
Modulation of Hair Growth Promoting Effect by Natural Products.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):2163. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122163. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Quail Yolk Oil via Upregulation of Superoxide Dismutase 1 and Catalase Genes and Downregulation of EIGER and Unpaired 2 Genes in a D. melanogaster Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;13(1):75. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010075. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247499 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical analysis and nephroprotective potential of Ajwa date in doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity rats: Biochemical and molecular docking approaches.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jan 27;11(3):1584-1598. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3199. eCollection 2023 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36911824 Free PMC article.
-
Current editorial challenges: Criteria for selecting articles for publication.EXCLI J. 2019 Dec 19;18:1101-1103. doi: 10.17179/excli2019-2076. eCollection 2019. EXCLI J. 2019. PMID: 31938030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Airanthi MKWA, Sasaki N, Iwasaki S, Baba N, Abe M, Hosokawa M, et al. Effect of brown seaweed lipids on fatty acid composition and lipid hydroperoxide levels of mouse liver. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59:4156–4163. - PubMed
-
- Ajizian SJ, English BK, Meals EA. Specific inhibitors of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways block inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor accumulation in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:939–944. - PubMed
-
- Bhat NR, Fan F. Adenovirus infection induces microglial activation: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Brain Res. 2002;948:1–2. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
