An approach for developing integrated undergraduate medical curriculum
- PMID: 30190732
- PMCID: PMC6115557
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.344.14565
An approach for developing integrated undergraduate medical curriculum
Abstract
Background and objectives: Medical schools are to develop integrated medical curricula because the term 'integrated curriculum' has grown up and flourished globally and it has become mandatory to align the medical education with the global concept in Pakistan. This paper aims to present a guideline to design an undergraduate integrated medical curriculum.
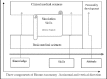
Methods: Various themes are used to develop integrated curriculum which are basic medical science, simulation skills, clinical science, personality development, research, entrepreneurship and pre specialization. Each theme is subdivided, termed a module and its contents primarily focus on particular aspect.
Results: Knowledge, skill and attitude, embodied in themes or modules, are planted in specific way that they have horizontal as well as vertical integration. There is no boundary of various traditional disciplines in template of five years curriculum. For example, diagnosis is a theme which carries contents from medicine, surgery, orthopedics etc.
Conclusion: The blueprint introduced in this paper would help medical educators to draft integrated medical curricula for those institutions which intend to switch their medical programs from traditional to integrated one.
Keywords: Basic sciences; Clinical science; Curriculum; Integration; Module; Undergraduate.
Figures
References
-
- David GB, Kristi JF. The integrated curriculum in medical education:AMEE Guide No.96. Med Teach. 2015;37(4):312–322. Doi:10.3109/0142159X.2014.970998. - PubMed
-
- Cook M, Irby DM, Sullivan W, Ludmerer KM. American medical education 100 years after the Flexner report. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(13):1339–1344. doi:10.1056/NEJMra055445. - PubMed
-
- Irby DM, Cooke M, O'Brien BC. Calls for reform of medical education by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching:1910 and 2010. Acad Med. 2010;85(2):220–227. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181c88449. - PubMed
-
- Finnerty EP, Chauvin S, Bonaminio G, Andrews M, Carroll RG, Pangaro LN. Flexner revisited:The role and value of the basic sciences in medical education. Acad Med. 2010;85(2):349–355. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181c88b09. - PubMed
-
- Maeshiro R, Johnson I, Koo D, Parboosingh J, Carney JK, Gesundheit N, et al. Medical education for a healthier population:Reflection on the Flexner report from a public health perspective. Acad Med. 2010;85(2):211–219. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181c885d8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources