Salivary glucose levels and oral candidal carriage in Type 2 diabetics
- PMID: 30191100
- PMCID: PMC6107908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2016.11.004
Salivary glucose levels and oral candidal carriage in Type 2 diabetics
Abstract
Background: To assess the correlation between salivary glucose and blood glucose levels in diabetics and non diabetics and to study the association between salivary glucose levels and oral candidal carriage in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Material and method: The study sample was divided into two groups, control and study group. The study group was again divided into two separate groups controlled diabetics and uncontrolled diabetics. Blood and saliva samples (for fasting and postprandial) were taken from each individual.
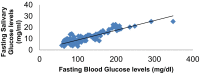
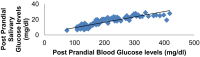
Results: The salivary glucose levels, highly correlated with blood glucose levels in both diabetic as well as non diabetics subjects. Salivary candidal carriage was more in oral cavity of Type 2 diabetic subjects than control subjects.
Conclusion: Saliva has the potential to be used as a noninvasive tool to monitor glycemic status of diabetic patients.
Keywords: Controlled diabetics (CD); Fasting blood glucose level (FBG); Non diabetics (ND); SGL (Salivary glucose level); Uncontrolled diabetics (UD).
Figures








References
-
- Marjani A. Effect of storage time and temperature on some serum analytes. Internet J Lab Med. 2006;(2):2.
-
- Aguirre F., Dahlquist G., Dodd T., Soltész G. 6th ed. International Diabetes Federation; 2013. IDF Diabetes Atlas: www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
-
- Joshi S.R., Parikh R.M. India: the diabetes capital of the world: now heading towards hypertension. J-Assoc Physicians India. 2007;55:323. - PubMed
-
- Guggenheimer J., Moore P.A., Rossie K. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and oral soft tissue pathologies, part II: prevalence and characteristics of Candida and candidal lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000;89:570–576. - PubMed
-
- Sashikumar R., Kannan R. Salivary glucose levels and oral candidal carriage in type II diabetics. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(5):706–711. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

