Modular Enzymatic Cascade Synthesis of Vitamin B5 and Its Derivatives
- PMID: 30192043
- PMCID: PMC6471175
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201804151
Modular Enzymatic Cascade Synthesis of Vitamin B5 and Its Derivatives
Abstract
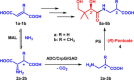
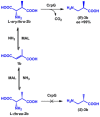
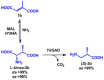
Access to vitamin B5 [(R)-pantothenic acid] and both diastereoisomers of α-methyl-substituted vitamin B5 [(R)- and (S)-3-((R)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido)-2-methylpropanoic acid] was achieved using a modular three-step biocatalytic cascade involving 3-methylaspartate ammonia lyase (MAL), aspartate-α-decarboxylase (ADC), β-methylaspartate-α-decarboxylase (CrpG) or glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), and pantothenate synthetase (PS) enzymes. Starting from simple non-chiral dicarboxylic acids (either fumaric acid or mesaconic acid), vitamin B5 and both diastereoisomers of α-methyl-substituted vitamin B5 , which are valuable precursors for promising antimicrobials against Plasmodium falciparum and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, can be generated in good yields (up to 70 %) and excellent enantiopurity (>99 % ee). This newly developed cascade process may be tailored and used for the biocatalytic production of various vitamin B5 derivatives by modifying the pantoyl or β-alanine moiety.
Keywords: biocatalysis; cascade reaction; enzymes; pantothenic acid.
© 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Spry C., Kirk K., Saliba K. J., FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 56–106. - PubMed
-
- Moolman W. J. A., de Villiers M., Strauss E., Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1080–1086. - PubMed
-
- de Villiers M., Barnard L., Koekemoer L., Snoep J. L., Strauss E., FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4731–4753. - PubMed
-
- Saliba K. J., Spry C., Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1087–1093. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

