Non-invasive measurement of mRNA decay reveals translation initiation as the major determinant of mRNA stability
- PMID: 30192227
- PMCID: PMC6152797
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.32536
Non-invasive measurement of mRNA decay reveals translation initiation as the major determinant of mRNA stability
Abstract
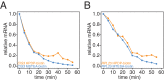
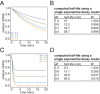
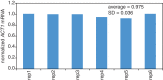
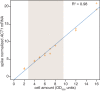
The cytoplasmic abundance of mRNAs is strictly controlled through a balance of production and degradation. Whereas the control of mRNA synthesis through transcription has been well characterized, less is known about the regulation of mRNA turnover, and a consensus model explaining the wide variations in mRNA decay rates remains elusive. Here, we combine non-invasive transcriptome-wide mRNA production and stability measurements with selective and acute perturbations to demonstrate that mRNA degradation is tightly coupled to the regulation of translation, and that a competition between translation initiation and mRNA decay -but not codon optimality or elongation- is the major determinant of mRNA stability in yeast. Our refined measurements also reveal a remarkably dynamic transcriptome with an average mRNA half-life of only 4.8 min - much shorter than previously thought. Furthermore, global mRNA destabilization by inhibition of translation initiation induces a dose-dependent formation of processing bodies in which mRNAs can decay over time.
Keywords: S. cerevisiae; chromosomes; decay; gene expression; genetics; genomics; mRNA; translation.
© 2018, Chan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LC, CM, SH, PV No competing interests declared, KW Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures





References
-
- Beelman CA, Parker R. Differential effects of translational inhibition in Cis and in trans on the decay of the unstable yeast MFA2 mRNA. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269:9687–9692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

