tp53 deficiency causes a wide tumor spectrum and increases embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma metastasis in zebrafish
- PMID: 30192230
- PMCID: PMC6128690
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.37202
tp53 deficiency causes a wide tumor spectrum and increases embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma metastasis in zebrafish
Abstract
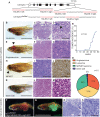
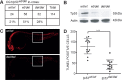
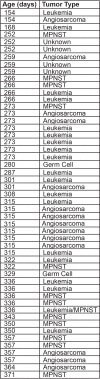
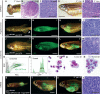
The TP53 tumor-suppressor gene is mutated in >50% of human tumors and Li-Fraumeni patients with germ line inactivation are predisposed to developing cancer. Here, we generated tp53 deleted zebrafish that spontaneously develop malignant peripheral nerve-sheath tumors, angiosarcomas, germ cell tumors, and an aggressive Natural Killer cell-like leukemia for which no animal model has been developed. Because the tp53 deletion was generated in syngeneic zebrafish, engraftment of fluorescent-labeled tumors could be dynamically visualized over time. Importantly, engrafted tumors shared gene expression signatures with predicted cells of origin in human tissue. Finally, we showed that tp53del/del enhanced invasion and metastasis in kRASG12D-induced embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS), but did not alter the overall frequency of cancer stem cells, suggesting novel pro-metastatic roles for TP53 loss-of-function in human muscle tumors. In summary, we have developed a Li-Fraumeni zebrafish model that is amenable to large-scale transplantation and direct visualization of tumor growth in live animals.
Keywords: MPNST; angiosarcoma; cancer biology; germ cell tumor; leukemia; metastasis; rhabdomyosarcoma; zebrafish.
© 2018, Ignatius et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MI, MH, FM, QT, SG, PB, KB, LW, AJ, AR, SR, YC, GN, EC, RH, FT, SE, DL No competing interests declared
Figures


References
-
- Andersen NJ, Nickoloff BJ, Dykema KJ, Boguslawski EA, Krivochenitser RI, Froman RE, Dawes MJ, Baker LH, Thomas DG, Kamstock DA, Kitchell BE, Furge KA, Duesbery NS. Pharmacologic inhibition of MEK signaling prevents growth of canine hemangiosarcoma. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2013;12:1701–1714. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0893. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen EY, DeRan MT, Ignatius MS, Grandinetti KB, Clagg R, McCarthy KM, Lobbardi RM, Brockmann J, Keller C, Wu X, Langenau DM. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors induce the canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway to suppress growth and self-renewal in embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma. PNAS. 2014;111:5349–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317731111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Stewart E, Shelat AA, Qu C, Bahrami A, Hatley M, Wu G, Bradley C, McEvoy J, Pappo A, Spunt S, Valentine MB, Valentine V, Krafcik F, Lang WH, Wierdl M, Tsurkan L, Tolleman V, Federico SM, Morton C, Lu C, Ding L, Easton J, Rusch M, Nagahawatte P, Wang J, Parker M, Wei L, Hedlund E, Finkelstein D, Edmonson M, Shurtleff S, Boggs K, Mulder H, Yergeau D, Skapek S, Hawkins DS, Ramirez N, Potter PM, Sandoval JA, Davidoff AM, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, Zhang J, Downing JR, Dyer MA, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital–Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project Targeting oxidative stress in embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:710–724. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.11.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24 OD016761/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R24OD016761/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154923/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA154923/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA215118/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024150/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM63904/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR160062/National Cancer Center/International
- Research Scholars Program/Massachusetts General Hospital/International
- R00CA175184/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA215118/National Cancer Center/International
- R01CA211734/National Cancer Center/International
- T32 CA148724/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA168512/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA211734/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063904/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA175184/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Amanda Riley Foundation Research Fellowship/Rally Foundation/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

