Macrocycle ring deformation as the secondary design principle for light-harvesting complexes
- PMID: 30194231
- PMCID: PMC6166793
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1719355115
Macrocycle ring deformation as the secondary design principle for light-harvesting complexes
Abstract
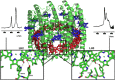
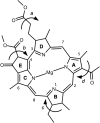
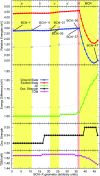
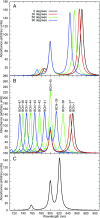
Natural light-harvesting is performed by pigment-protein complexes, which collect and funnel the solar energy at the start of photosynthesis. The identity and arrangement of pigments largely define the absorption spectrum of the antenna complex, which is further regulated by a palette of structural factors. Small alterations are induced by pigment-protein interactions. In light-harvesting systems 2 and 3 from Rhodoblastus acidophilus, the pigments are arranged identically, yet the former has an absorption peak at 850 nm that is blue-shifted to 820 nm in the latter. While the shift has previously been attributed to the removal of hydrogen bonds, which brings changes in the acetyl moiety of the bacteriochlorophyll, recent work has shown that other mechanisms are also present. Using computational and modeling tools on the corresponding crystal structures, we reach a different conclusion: The most critical factor for the shift is the curvature of the macrocycle ring. The bending of the planar part of the pigment is identified as the second-most important design principle for the function of pigment-protein complexes-a finding that can inspire the design of novel artificial systems.
Keywords: LH3; MS-RASPT2; bacteriochlorophyll; chromophore mimics; macrocycle ring deformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dostál J, Pšenčík J, Zigmantas D. In situ mapping of the energy flow through the entire photosynthetic apparatus. Nat Chem. 2016;8:705–710. - PubMed
-
- Fuller FD, et al. Vibronic coherence in oxygenic photosynthesis. Nat Chem. 2014;6:706–711. - PubMed
-
- Timpmann K, et al. Short-range exciton couplings in LH2 photosynthetic antenna proteins studied by high hydrostatic pressure absorption spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:8436–8444.
-
- Plenio MB, Huelga SF. Dephasing-assisted transport: Quantum networks and biomolecules. New J Phys. 2008;10:113019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

