Sodium and potassium conductances in principal neurons of the mouse piriform cortex: a quantitative description
- PMID: 30194865
- PMCID: PMC6235943
- DOI: 10.1113/JP275824
Sodium and potassium conductances in principal neurons of the mouse piriform cortex: a quantitative description
Abstract
Key points: The primary olfactory (or piriform) cortex is a promising model system for understanding how the cerebral cortex processes sensory information, although an investigation of the piriform cortex is hindered by a lack of detailed information about the intrinsic electrical properties of its component neurons. In the present study, we quantify the properties of voltage-dependent sodium currents and voltage- and calcium-dependent potassium currents in two important classes of excitatory neurons in the main input layer of the piriform cortex. We identify several classes of these currents and show that their properties are similar to those found in better-studied cortical regions. Our detailed quantitative descriptions of these currents will be valuable to computational neuroscientists who aim to build models that explain how the piriform cortex encodes odours.
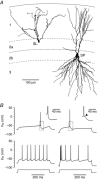
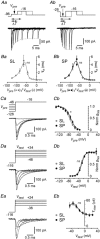
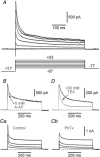
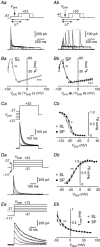
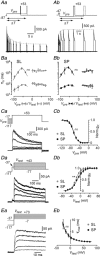
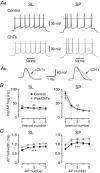
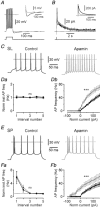
Abstract: The primary olfactory cortex (or piriform cortex, PC) is an anatomically simple palaeocortex that is increasingly used as a model system for investigating cortical sensory processing. However, little information is available on the intrinsic electrical conductances in neurons of the PC, hampering efforts to build realistic computational models of this cortex. In the present study, we used nucleated macropatches and whole-cell recordings to rigorously quantify the biophysical properties of voltage-gated sodium (NaV ), voltage-gated potassium (KV ) and calcium-activated potassium (KCa ) conductances in two major classes of glutamatergic neurons in layer 2 of the PC, semilunar (SL) cells and superficial pyramidal (SP) cells. We found that SL and SP cells both express a fast-inactivating NaV current, two types of KV current (A-type and delayed rectifier-type) and three types of KCa current (fast-, medium- and slow-afterhyperpolarization currents). The kinetic and voltage-dependent properties of the NaV and KV conductances were, with some exceptions, identical in SL and SP cells and similar to those found in neocortical pyramidal neurons. The KCa conductances were also similar across the different types of neurons. Our results are summarized in a series of empirical equations that should prove useful to computational neuroscientists seeking to model the PC. More broadly, our findings indicate that, at the level of single-cell electrical properties, this palaeocortex is not so different from the neocortex, vindicating efforts to use the PC as a model of cortical sensory processing in general.
Keywords: Hodgkin-Huxley analysis; olfactory cortex; patch clamp.
© 2018 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2018 The Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural coding by two classes of principal cells in the mouse piriform cortex.J Neurosci. 2006 Nov 15;26(46):11938-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3473-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17108168 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental changes in Na+ conductances in rat neocortical neurons: appearance of a slowly inactivating component.J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):778-95. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.778. J Neurophysiol. 1988. PMID: 2452862
-
Optogenetic Mapping of Intracortical Circuits Originating from Semilunar Cells in the Piriform Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2017 Jan 1;27(1):589-601. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv258. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 26503263 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-dependent currents of vertebrate neurons and their role in membrane excitability.Adv Neurol. 1986;44:137-70. Adv Neurol. 1986. PMID: 2422889 Review.
-
Ionic channel function in action potential generation: current perspective.Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Apr;35(2):129-50. doi: 10.1007/s12035-007-8001-0. Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17917103 Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent Na+ current couples spreading depolarization to seizures in Scn8a gain of function mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 23:2024.10.11.617888. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.11.617888. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Brain. 2025 Apr 03:awaf120. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf120. PMID: 39416109 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Olfactory dysfunction and altered cortical excitability in the mouse model of Fragile X Syndrome.Biol Res. 2025 Apr 24;58(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00582-2. Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 40275427 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Kv1.3 knockout on pyramidal neuron excitability and synaptic plasticity in piriform cortex of mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Oct;45(10):2045-2060. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01275-y. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38862816
-
Autaptic Cultures: Methods and Applications.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020 Apr 30;12:18. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2020.00018. eCollection 2020. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32425765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bekkers JM & Suzuki N (2013). Neurons and circuits for odor processing in the piriform cortex. Trends Neurosci 36, 429–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

