Plasma Amyloid as Prescreener for the Earliest Alzheimer Pathological Changes
- PMID: 30196548
- PMCID: PMC6282982
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25334
Plasma Amyloid as Prescreener for the Earliest Alzheimer Pathological Changes
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the association of plasma amyloid beta (Abeta)40, Abeta42, and total tau (tTau) with the presence of Alzheimer pathological changes in cognitively normal individuals with subjective cognitive decline (SCD).
Methods: We included 248 subjects with SCD (61 ± 9 years, 42% female, Mini-Mental State Examination = 28 ± 2) from the SCIENCe project and Amsterdam Dementia Cohort. Subjects were dichotomized as amyloid abnormal by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and positron emission tomography (PET). Baseline plasma Abeta40, Abeta42, and tTau were measured using Simoa technology. Associations between plasma levels and amyloid status were assessed using logistic regression analyses and receiver operating characteristic analyses. Association of plasma levels with risk of clinical progression to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia was assessed using Cox proportional hazard models.
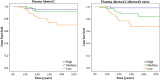
Results: Fifty-seven (23%) subjects were CSF-amyloid abnormal. Plasma Abeta42/Abeta40 ratio and plasma Abeta42 alone, but not tTau, identified abnormal CSF-amyloid status (plasma ratio: area under the curve [AUC] = 77%, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 69-84%; plasma Abeta42: AUC = 66%, 95% CI: 58-74%). Combining plasma ratio with age and apolipoprotein E resulted in AUC = 83% (95% CI = 77-89%). The Youden cutoff of the plasma ratio gave a sensitivity of 76% and specificity of 75%, and applying this as a prescreener would reduce the number of lumbar punctures by 51%. Using PET as outcome, a comparable reduction in number of PET scans would be achieved when applying the plasma ratio as prescreener. In addition, low plasma ratio was associated with clinical progression to MCI or dementia (hazard ratio = 2.0, 95% CI = 1.4-2.3).
Interpretation: Plasma Abeta42/Abeta40 ratio has potential as a prescreener to identify Alzheimer pathological changes in cognitively normal individuals with SCD. Ann Neurol 2018;84:656-666.
© 2018 The Authors. Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Figures




Comment in
-
Reply to "Usefulness of Plasma Amyloid as Prescreener of the Earliest Alzheimer Pathological Changes Depends on the Study Population".Ann Neurol. 2020 Jan;87(1):155. doi: 10.1002/ana.25633. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Ann Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31675120 No abstract available.
-
Usefulness of Plasma Amyloid as a Prescreener for the Earliest Alzheimer Pathological Changes Depends on the Study Population.Ann Neurol. 2020 Jan;87(1):154-155. doi: 10.1002/ana.25634. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Ann Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31675127 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

