Variability in PolyIC induced immune response: Implications for preclinical maternal immune activation models
- PMID: 30196839
- PMCID: PMC6782055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.06.014
Variability in PolyIC induced immune response: Implications for preclinical maternal immune activation models
Abstract
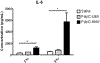
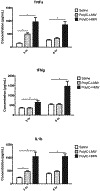
Maternal infection during pregnancy may increase the risk of offspring neurodevelopmental disorders. The preclinical Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (PolyIC) model has become one of the most widely used approaches in maternal immune activation (MIA) research. However, variability in molecular weight may impact the immune activating potential of PolyIC. Nulliparous rats injected with high molecular weight PolyIC exhibit pronounced cytokine response and sickness behavior that was not observed in rats injected low molecular weight PolyIC. Although an essential next step is to extend these studies to pregnant animals, the preliminary results suggest that PolyIC molecular weight is an important experimental design consideration.
Keywords: Cytokine; Immune; Maternal immune activation; PolyIC; Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid; Sickness behavior.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
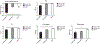
Similar articles
-
Maternal immune activation with high molecular weight poly(I:C) in Wistar rats leads to elevated immune cell chemoattractants.J Neuroimmunol. 2022 Mar 15;364:577813. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2022.577813. Epub 2022 Jan 14. J Neuroimmunol. 2022. PMID: 35093761
-
Poly(I:C) source, molecular weight and endotoxin contamination affect dam and prenatal outcomes, implications for models of maternal immune activation.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Nov;82:160-166. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 31415868
-
Prenatal immune challenge in rats: effects of polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid on spatial learning, prepulse inhibition, conditioned fear, and responses to MK-801 and amphetamine.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2015 Jan-Feb;47:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2014.10.007. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2015. PMID: 25450663 Free PMC article.
-
The poly(I:C)-induced maternal immune activation model in preclinical neuropsychiatric drug discovery.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 May;149:213-26. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 4. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25562580 Review.
-
The poly(I:C)-induced maternal immune activation model; a systematic review and meta-analysis of cytokine levels in the offspring.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020 Dec 19;11:100192. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100192. eCollection 2021 Feb. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020. PMID: 34589729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influences of the Immune System and Microbiome on the Etiology of ASD and GI Symptomology of Autistic Individuals.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023;61:141-161. doi: 10.1007/7854_2022_371. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 35711026
-
A comprehensive approach to modeling maternal immune activation in rodents.Front Neurosci. 2022 Dec 16;16:1071976. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1071976. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36590294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin 15 modulates the effects of poly I:C maternal immune activation on offspring behaviour.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 May 18;23:100473. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100473. eCollection 2022 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 35668725 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal immune activation in rats induces dysfunction of placental leucine transport and alters fetal brain growth.Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Aug 12;136(15):1117-1137. doi: 10.1042/CS20220245. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35852150 Free PMC article.
-
Increased alcohol self-administration following repeated Toll-like receptor 3 agonist treatment in male and female rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 May;216:173379. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173379. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35395252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexopoulou L, et al., 2001. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413 (6857), 732–738. - PubMed
-
- Begley CG, Ioannidis JP, 2015. Reproducibility in science: improving the standard for basic and preclinical research. Circ. Res. 116 (1), 116–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

