Inactivation of PLK4-STIL Module Prevents Self-Renewal and Triggers p53-Dependent Differentiation in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 30197118
- PMCID: PMC6178195
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.08.008
Inactivation of PLK4-STIL Module Prevents Self-Renewal and Triggers p53-Dependent Differentiation in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
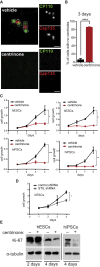
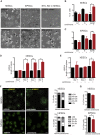
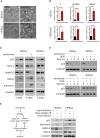
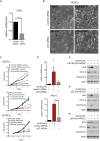
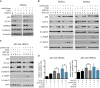
Centrioles account for centrosomes and cilia formation. Recently, a link between centrosomal components and human developmental disorders has been established. However, the exact mechanisms how centrosome abnormalities influence embryogenesis and cell fate are not understood. PLK4-STIL module represents a key element of centrosome duplication cycle. We analyzed consequences of inactivation of the module for early events of embryogenesis in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs). We demonstrate that blocking of PLK4 or STIL functions leads to centrosome loss followed by both p53-dependent and -independent defects, including prolonged cell divisions, upregulation of p53, chromosome instability, and, importantly, reduction of pluripotency markers and induction of differentiation. We show that the observed loss of key stem cells properties is connected to alterations in mitotic timing and protein turnover. In sum, our data define a link between centrosome, its regulators, and the control of pluripotency and differentiation in PSCs.
Keywords: acentrosomal; cell cycle; centriole; centrosome; differentiation; pluripotency; self-renewal; stem cell.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CDK1 Prevents Unscheduled PLK4-STIL Complex Assembly in Centriole Biogenesis.Curr Biol. 2016 May 9;26(9):1127-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.055. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27112295 Free PMC article.
-
STIL is required for centriole duplication in human cells.J Cell Sci. 2012 Mar 1;125(Pt 5):1353-62. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104109. Epub 2012 Feb 20. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22349705
-
Binding of STIL to Plk4 activates kinase activity to promote centriole assembly.J Cell Biol. 2015 Jun 22;209(6):863-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201502088. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26101219 Free PMC article.
-
The PLK4-STIL-SAS-6 module at the core of centriole duplication.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Oct 15;44(5):1253-1263. doi: 10.1042/BST20160116. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27911707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The centrosome duplication cycle in health and disease.FEBS Lett. 2014 Aug 1;588(15):2366-72. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.06.030. Epub 2014 Jun 18. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24951839 Review.
Cited by
-
KIF14 controls ciliogenesis via regulation of Aurora A and is important for Hedgehog signaling.J Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 1;219(6):e201904107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201904107. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32348467 Free PMC article.
-
Tau tubulin kinase 1 and 2 regulate ciliogenesis and human pluripotent stem cells-derived neural rosettes.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 9;13(1):12884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39887-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37558899 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11 endosomes and Pericentrin coordinate centrosome movement during pre-abscission in vivo.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Mar 18;5(7):e202201362. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201362. Print 2022 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 35304423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adewumi O., Aflatoonian B., Ahrlund-Richter L., Amit M., Andrews P.W., Beighton G., Bello P.A., Benvenisty N., Berry L.S., Bevan S. Characterization of human embryonic stem cell lines by the International Stem Cell Initiative. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007;25:803–816. - PubMed
-
- Aladjem M.I., Spike B.T., Rodewald L.W., Hope T.J., Klemm M., Jaenisch R., Wahl G.M. ES cells do not activate p53-dependent stress responses and undergo p53- independent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:145–155. - PubMed
-
- Andersen J.S., Wilkinson C.J., Mayor T., Mortensen P., Nigg E.A., Mann M. Proteomic characterization of the human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nature. 2003;426:570–574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

