Anxiety Specific Response and Contribution of Active Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells to Chronic Pain Through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mice
- PMID: 30197587
- PMCID: PMC6117500
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00296
Anxiety Specific Response and Contribution of Active Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells to Chronic Pain Through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mice
Abstract
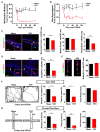
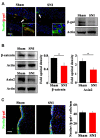
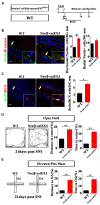
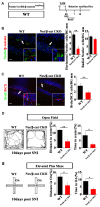
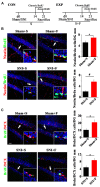
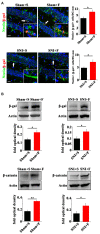
Chronic pain usually results in persistent anxiety, which worsens the life quality of patients and complicates the treatment of pain. Hippocampus is one of the few brain regions in many mammalians species which harbors adult neural stem cells (NSCs), and plays a key role in the development and maintenance of chronic anxiety. Recent studies have suggested a potential involvement of hippocampal neurogenesis in modulating chronic pain. Whether and how hippocampal NSCs are involved in the pain-associated anxiety remains unclear. Here, we report that mice suffering persistent neuropathic pain showed a quick reduction of active NSCs in the ventral dentate gyrus (vDG), which was followed by the decrease of neurogenesis and appearance of anxiety. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a key pathway in sustaining the active status of NSCs was suppressed in the vDG of mice suffering chronic pain. Depleting β-catenin by inducible Nestin-Cre significantly reduced the number of active NSCs and facilitated anxiety development, while expressing stabilized β-catenin amplified active NSCs and alleviated anxiety, indicating that Wnt activated NSCs is required for anxiety development under chronic pain. Treatment with Fluoxetine, the most widely used anxiolytic in clinic, significantly increased the proliferation of active NSCs and enhanced Wnt signaling. Interestingly, both β-catenin manipulation and Fluoxetine treatment had no significant effects on the pain thresholds. Therefore, our data demonstrated an anxiety-specific response and contribution of activated NSCs to chronic pain through Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which may be targeted for treating chronic pain- or other diseases-associated anxiety.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin signaling; adult neural stem cell; anxiety; chronic pain; hippocampus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wnt/β-catenin signalling is dispensable for adult neural stem cell homeostasis and activation.Development. 2021 Oct 15;148(20):dev199629. doi: 10.1242/dev.199629. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Development. 2021. PMID: 34557919 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Stem Cells Secretome Increased Neurogenesis and Behavioral Performance and the Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2022 Dec;24(4):424-436. doi: 10.1007/s12017-022-08708-z. Epub 2022 May 16. Neuromolecular Med. 2022. PMID: 35576045
-
Effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 Regulating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling on Neural Stem Cells to Delay Brain Senescence.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Dec 4;2019:5010184. doi: 10.1155/2019/5010184. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31885611 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of β-catenin signaling on neurogenesis in neuropsychiatric disorders: Anxiety and depression.Drug Dev Res. 2024 Feb;85(1):e22157. doi: 10.1002/ddr.22157. Drug Dev Res. 2024. PMID: 38349261 Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomers: Novel Strategy for Endogenous Neural Stem Cells Activation After Stroke.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Feb 26;15:628115. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.628115. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vilazodone Alleviates Neurogenesis-Induced Anxiety in the Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Female Rat Model: Role of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9060-9077. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04142-3. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38584231 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine Rescues Excessive Myelin Formation and Psychological Behaviors in a Murine PTSD Model.Neurosci Bull. 2024 Aug;40(8):1037-1052. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01249-4. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 39014176 Free PMC article.
-
Ablated Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in the Dentate Gyrus of the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Impairs Hippocampal-Dependent Memory Tasks and Emotion in a Rat Model of Depression.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4352-4368. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03796-9. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38087166
-
Effects of Septin-14 Gene Deletion on Adult Cognitive/Emotional Behavior.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Apr 29;15:880858. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.880858. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35571367 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrations in the Cross-Talks Among Redox, Nuclear Factor-κB, and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Signaling Underpin Myalgic Encephalomyelitis and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.Front Psychiatry. 2022 May 6;13:822382. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.822382. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35599774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brault V., Moore R., Kutsch S., Ishibashi M., Rowitch D. H., McMahon A. P., et al. . (2001). Inactivation of the β-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cre-mediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development. Development 128, 1253–1264. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

