Control of Germinal Center Responses by T-Follicular Regulatory Cells
- PMID: 30197643
- PMCID: PMC6117393
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01910
Control of Germinal Center Responses by T-Follicular Regulatory Cells
Abstract
Regulatory T-cells (Treg cells), expressing the transcription factor Foxp3, have an essential role in the control of immune homeostasis. In order to control diverse types of immune responses Treg cells must themselves show functional heterogeneity to control different types of immune responses. Recent advances have made it clear that Treg cells are able to mirror the homing capabilities of known T-helper subtypes such as Th1, Th2, Th17, and T-follicular helper cells (Tfh), allowing them to travel to the sites of inflammation and deliver suppression in situ. One of the more recent discoveries in this category is the description of T-follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells, a specialized subset of Treg cells that control Tfh and resulting antibody responses. In this review we will discuss recent advances in our understanding of Tfr biology and the role of both Tfr and activated extra-follicular Tregs (eTreg) in the control of humoral immunity.
Keywords: T follicular helper (Tfh) cell; T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cell; autoimmunity; germinal center (GC); regulatory T-cells (Tregs).
Figures
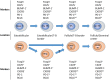
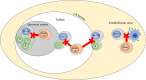
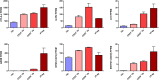
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

