Disseminated Strongyloidiasis in Association with Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 30197904
- PMCID: PMC6120380
- DOI: 10.1159/000491632
Disseminated Strongyloidiasis in Association with Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
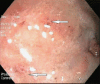
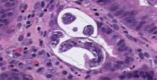
Strongyloidiasis is a well-known parasitic infection endemic in tropical and subtropical areas of the world. While most infected individuals are asymptomatic, strongyloidiasis-related glomerulopathy has not been well documented. We present a case of disseminated strongyloidiasis in a patient with minimal change nephrotic syndrome treated with high-dose corticosteroids. The remission of nephrotic syndrome after treatment of strongyloidiasis suggests a possible causal relationship between Strongyloides and nephrotic syndrome.
Keywords: Nephrotic syndrome; Strongyloides stercoralis; Strongyloidiasis.
Figures
References
-
- Chaudhary K, Smith RJ, Himelright IM, Baddour LM. Case report: purpura in disseminated strongyloidiasis. Am J Med Sci. 1994 Sep;308((3)):186–91. - PubMed
-
- Owor R, Wamukota WM. A fatal case of strongyloidiasis with Strongyloides larvae in the meninges. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1976;70((5–6)):497–9. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh YP, Wen YK, Chen ML. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome in association with strongyloidiasis. Clin Nephrol. 2006 Dec;66((6)):459–63. - PubMed
-
- Churg J, Sobin LH. Tokyo: Igaku-Shoin; 1982. Renal Disease: Classification and Atlas of Glomerular Diseases.
-
- Purtilo DT, Meyers WM, Connor DH. Fatal strongyloidiasis in immunosuppressed patients. Am J Med. 1974 Apr;56((4)):488–93. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources