Contribution of NK cells to immunotherapy mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 blockade
- PMID: 30198904
- PMCID: PMC6159991
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI99317
Contribution of NK cells to immunotherapy mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 blockade
Abstract
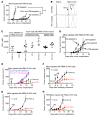
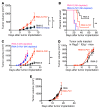
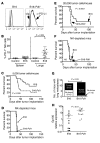
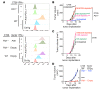
Checkpoint blockade immunotherapy targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory axis has produced remarkable results in the treatment of several types of cancer. Whereas cytotoxic T cells are known to provide important antitumor effects during checkpoint blockade, certain cancers with low MHC expression are responsive to therapy, suggesting that other immune cell types may also play a role. Here, we employed several mouse models of cancer to investigate the effect of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade on NK cells, a population of cytotoxic innate lymphocytes that also mediate antitumor immunity. We discovered that PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade elicited a strong NK cell response that was indispensable for the full therapeutic effect of immunotherapy. PD-1 was expressed on NK cells within transplantable, spontaneous, and genetically induced mouse tumor models, and PD-L1 expression in cancer cells resulted in reduced NK cell responses and generation of more aggressive tumors in vivo. PD-1 expression was more abundant on NK cells with an activated and more responsive phenotype and did not mark NK cells with an exhausted phenotype. These results demonstrate the importance of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in inhibiting NK cell responses in vivo and reveal that NK cells, in addition to T cells, mediate the effect of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy.
Keywords: Immunology; Immunotherapy; Innate immunity; NK cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
NK cells for PD-1/PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy: pinning down the NK cell.J Clin Invest. 2018 Oct 1;128(10):4251-4253. doi: 10.1172/JCI123121. Epub 2018 Sep 10. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30198909 Free PMC article.
-
NK Cells Respond to Checkpoint Blockade.Cancer Discov. 2018 Dec;8(12):1498. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2018-131. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Cancer Discov. 2018. PMID: 30352860
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

