Growth hormone secretagogue receptor constitutive activity impairs voltage-gated calcium channel-dependent inhibitory neurotransmission in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 30199095
- PMCID: PMC6235945
- DOI: 10.1113/JP276256
Growth hormone secretagogue receptor constitutive activity impairs voltage-gated calcium channel-dependent inhibitory neurotransmission in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
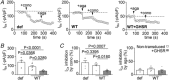
Key points: Presynaptic CaV 2 voltage-gated calcium channels link action potentials arriving at the presynaptic terminal to neurotransmitter release. Hence, their regulation is essential to fine tune brain circuitry. CaV 2 channels are highly sensitive to G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) modulation. Our previous data indicated that growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) constitutive activity impairs CaV 2 channels by decreasing their surface density. We present compelling support for the impact of CaV 2.2 channel inhibition by agonist-independent GHSR activity exclusively on GABA release in hippocampal cultures. We found that this selectivity arises from a high reliance of GABA release on CaV 2.2 rather than on CaV 2.1 channels. Our data provide new information on the effects of the ghrelin-GHSR system on synaptic transmission, suggesting a putative physiological role of the constitutive signalling of a GPCR that is expressed at high levels in brain areas with restricted access to its natural agonist.
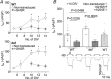
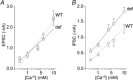
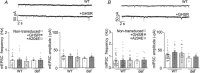
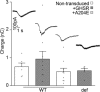
Abstract: Growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) displays high constitutive activity, independent of its endogenous ligand, ghrelin. Unlike ghrelin-induced GHSR activity, the physiological role of GHSR constitutive activity and the mechanisms that underlie GHSR neuronal modulation remain elusive. We previously demonstrated that GHSR constitutive activity modulates presynaptic CaV 2 voltage-gated calcium channels. Here we postulate that GHSR constitutive activity-mediated modulation of CaV 2 channels could be relevant in the hippocampus since this brain area has high GHSR expression but restricted access to ghrelin. We performed whole-cell patch-clamp in hippocampal primary cultures from E16- to E18-day-old C57BL6 wild-type and GHSR-deficient mice after manipulating GHSR expression with lentiviral transduction. We found that GHSR constitutive activity impairs CaV 2.1 and CaV 2.2 native calcium currents and that CaV 2.2 basal impairment leads to a decrease in GABA but not glutamate release. We postulated that this selective effect is related to a higher CaV 2.2 over CaV 2.1 contribution to GABA release (∼40% for CaV 2.2 in wild-type vs. ∼20% in wild-type GHSR-overexpressing cultures). This effect of GHSR constitutive activity is conserved in hippocampal brain slices, where GHSR constitutive activity reduces local GABAergic transmission of the granule cell layer (intra-granule cell inhibitory postsynaptic current (IPSC) size ∼-67 pA in wild-type vs. ∼-100 pA in GHSR-deficient mice), whereas the glutamatergic output from the dentate gyrus to CA3 remains unchanged. In summary, we found that GHSR constitutive activity impairs IPSCs both in hippocampal primary cultures and in brain slices through a CaV 2-dependent mechanism without affecting glutamatergic transmission.
Keywords: GABA; GPCR; Synapse; brain slices; electrophysiology; ghrelin; inhibitory postsynaptic current; primary cultures.
© 2018 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2018 The Physiological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Abizaid A (2011). Motivation to obtain preferred foods is enhanced by ghrelin in the ventral tegmental area. Horm Behav 60, 572–580. - PubMed
-
- Agosti F, Cordisco Gonzalez S, Martinez Damonte V, Tolosa M J, Di Siervi N, Schioth HB, Davio C, Perello M & Raingo J (2017). Melanocortin 4 receptor constitutive activity inhibits L‐type voltage‐gated calcium channels in neurons. Neuroscience 346, 102–112. - PubMed
-
- Atcha Z, Chen W‐S, Ong AB, Wong F‐K, Neo A, Browne ER, Witherington J & Pemberton DJ (2009). Cognitive enhancing effects of ghrelin receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 206, 415–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

