Phosphonamidate Prodrugs of a Butyrophilin Ligand Display Plasma Stability and Potent Vγ9 Vδ2 T Cell Stimulation
- PMID: 30199251
- PMCID: PMC6703555
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00655
Phosphonamidate Prodrugs of a Butyrophilin Ligand Display Plasma Stability and Potent Vγ9 Vδ2 T Cell Stimulation
Abstract
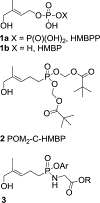
Small organophosphorus compounds stimulate Vγ9 Vδ2 T cells if they serve as ligands of butyrophilin 3A1. Because the most potent natural ligand is ( E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl diphosphate (HMBPP), which is the last intermediate in bacterial biosynthesis of isoprenoids that is not found in mammalian metabolism, activation of these T cells represents an important component of the immune response to bacterial infections. To identify butyrophilin ligands that may have greater plasma stability, and clinical potential, we have prepared a set of aryl phosphonamidate derivatives (9a-i) of the natural ligand. Testing of these new compounds in assays of T cell response has revealed that this strategy can provide compounds with high potency for expansion of Vγ9 Vδ2 T cells (9f, EC50 = 340 pM) and interferon γ production in response to loaded K562 cells (9e, EC50 = 62 nM). Importantly, all compounds of this class display extended plasma stability ( t1/2 > 24 h). These findings increase our understanding of metabolism of butyrophilin ligands and the structure-activity relationships of phosphonamidate prodrugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Aryloxy Diester Phosphonamidate Prodrugs of Phosphoantigens (ProPAgens) as Potent Activators of Vγ9/Vδ2 T-Cell Immune Responses.J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 8;63(19):11258-11270. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01232. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32930595 Free PMC article.
-
Diester Prodrugs of a Phosphonate Butyrophilin Ligand Display Improved Cell Potency, Plasma Stability, and Payload Internalization.J Med Chem. 2023 Nov 23;66(22):15309-15325. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01358. Epub 2023 Nov 7. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37934915 Free PMC article.
-
Potent double prodrug forms of synthetic phosphoantigens.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Oct 1;28(19):115666. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115666. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32912439 Free PMC article.
-
Non-peptide antigens activating human Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes.Immunol Lett. 2004 Sep;95(2):129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.06.013. Immunol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15388252 Review.
-
Structure-Activity Relationships of Butyrophilin 3 Ligands.ChemMedChem. 2020 Jun 17;15(12):1030-1039. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000198. Epub 2020 May 26. ChemMedChem. 2020. PMID: 32453919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporation of a FRET pair within a phosphonate diester.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Sep;114:105048. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105048. Epub 2021 May 30. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34126576 Free PMC article.
-
Prodrugs of a 1-Hydroxy-2-oxopiperidin-3-yl Phosphonate Enolase Inhibitor for the Treatment of ENO1-Deleted Cancers.J Med Chem. 2022 Oct 27;65(20):13813-13832. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01039. Epub 2022 Oct 17. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36251833 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of bis-amidate phosphonate prodrugs.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Jun 15;66:128724. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128724. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35405283 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Bioactivity of the Alanyl Phosphonamidate Stereoisomers Derived from a Butyrophilin Ligand.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019 Aug 6;10(9):1284-1289. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00153. eCollection 2019 Sep 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31531198 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Metabolism of BTN3A1 Ligands: Studies on Modifications of the Allylic Alcohol.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Dec 4;12(1):136-142. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00586. eCollection 2021 Jan 14. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 33488975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhodes DA; Reith W; Trowsdale J Regulation of Immunity by Butyrophilins - PubMed
-
- Gu S; Borowska M; Boughter CT; Adams EJ Butyrophilin3a Proteins and Vgamma9vdelta2 T Cell Activation Semin Cell Dev Biol [Online early access] DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.02.007 . Published Online: March 9 2018 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.02.007https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084952116304360?via%.... Published Online: March 9 2018 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084952116304360?via%... (accessed July 26, 2018) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wiemer DF; Wiemer AJ Opportunities and Challenges in Development of Phosphoantigens as Vgamma9vdelta2 T Cell Agonists Biochem. Pharmacol 2014, 89, 301–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

