Topical and systemic antifungal therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 30199594
- PMCID: PMC6513454
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012453.pub2
Topical and systemic antifungal therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: This review adds to a series of reviews looking at primary medical management options for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis.Chronic rhinosinusitis is common and characterised by inflammation of the lining of the nose and paranasal sinuses leading to nasal blockage, nasal discharge, facial pressure/pain and loss of sense of smell. The condition can occur with or without nasal polyps. Antifungals have been suggested as a treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis.
Objectives: To assess the effects of systemic and topical antifungal agents in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis, including those with allergic fungal rhinosinusitis (AFRS) and, if possible, AFRS exclusively.
Search methods: The Cochrane ENT Information Specialist searched the Cochrane ENT Trials Register; Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); Ovid MEDLINE; Ovid Embase; CINAHL; Web of Science; ClinicalTrials.gov; ICTRP and additional sources for published and unpublished trials. The date of the search was 17 November 2017.
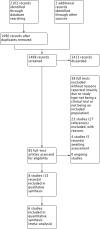
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) with at least a two-week follow-up period comparing topical or systemic antifungals with (a) placebo, (b) no treatment, (c) other pharmacological interventions or (d) a different antifungal agent. We did not include post-surgical antifungal use.
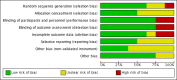
Data collection and analysis: We used the standard Cochrane methodological procedures. Our primary outcomes were disease-specific health-related quality of life (HRQL), patient-reported disease severity and the significant adverse effects of hepatic toxicity (systemic antifungals). Secondary outcomes included general HRQL, endoscopic nasal polyp score, computerised tomography (CT) scan score and the adverse effects of gastrointestinal disturbance (systemic antifungals) and epistaxis, headache or local discomfort (topical antifungals). We used GRADE to assess the quality of the evidence for each outcome; this is indicated in italics.
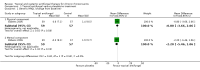
Main results: We included eight studies (490 adult participants). The presence of nasal polyps on examination was an inclusion criterion in three studies, an exclusion criterion in one study and the remaining studies included a mixed population. No studies specifically investigated the effect of antifungals in patients with AFRS.Topical antifungal treatment versus placebo or no interventionWe included seven studies (437 participants) that used amphotericin B (six studies; 383 participants) and one that used fluconazole (54 participants). Different delivery methods, volumes and concentrations were used.Four studies reported disease-specific health-related quality of life using a range of instruments. We did not meta-analyse the results due to differences in the instruments used, and measurement and reporting methods. At the end of treatment (one to six months) none of the studies reported statistically significant differences between the groups (low-quality evidence - we are uncertain about the result).Two studies reported disease severity using patient-reported symptom scores. Meta-analysis was not possible. At the end of treatment (8 to 13 weeks) one study showed no difference and the second found that patients in the placebo group had less severe symptoms (very low-quality evidence - we are very uncertain about the result).In terms of adverse effects, topical antifungals may lead to more local irritation compared with placebo (risk ratio (RR) 2.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.61 to 8.62; 312 participants; 5 studies; low-quality evidence) but little or no difference in epistaxis (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.14 to 6.63; 225 participants; 4 studies, low-quality evidence) or headache (RR 1.26, 95% CI 0.60 to 2.63; 195 participants; 3 studies; very low-quality evidence).None of the studies found a difference in generic health-related quality of life (one study) or endoscopic score (five studies) between the treatment groups. Three studies investigated CT scan; two found no difference between the groups and one found a significant decrease in the mean percentage of air space occluded, favouring the antifungal group.Systemic antifungal treatment versus placebo or no treatmentOne study (53 participants) comparing terbinafine tablets against placebo reported that there may be little or no difference between the groups in disease-specific health-related quality of life or disease severity score (both low-quality evidence). Systemic antifungals may lead to more hepatic toxicity events (RR 3.35, 95% CI 0.14 to 78.60) but fewer gastrointestinal disturbances (RR 0.37, 95% CI 0.04 to 3.36), compared to placebo, although the evidence was of low quality.This study did not find a difference in CT scan score between the groups. Generic health-related quality of life and endoscopic score were not measured.Other comparisonsWe found no studies that compared antifungal agents against other treatments for chronic rhinosinusitis.
Authors' conclusions: Due to the very low quality of the evidence, it is uncertain whether or not the use of topical or systemic antifungals has an impact on patient outcomes in adults with chronic rhinosinusitis compared with placebo or no treatment. Studies including specific subgroups (i.e. AFRS) are lacking.
Conflict of interest statement
Karen Head: none known.
Steve Sharp: none known.
Lee Yee Chong: none known.
Claire Hopkins: I have received financial support from several companies involved in producing instruments for sinus surgery: Acclarent, Sinusys, Cryolife and Medtronic.
Carl Philpott: I have previously received consultancy fees from the companies Acclarent, Navigant, Aerin Medical and Entellus, and am a trustee of the patient charity Fifth Sense.
Figures
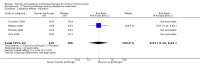
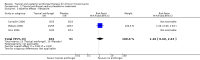
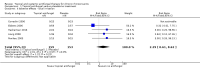





Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
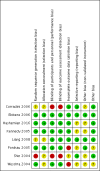
Corradini 2006 {published data only}
-
- Corradini C, Ninno M, Buonomo A, Nucera E, Paludetti G, Alonzi C, et al. Amphotericin B and lysine acetylsalicylate in the combined treatment of nasal polyposis associated with mycotic infection. Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology 2006;16(3):188‐93. [CENTRAL: CN‐00570817; CRS: 1400041; EMBASE: 2006292109; PUBMED: 16784013] - PubMed
Ebbens 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ebbens FA, Bachert C, Mullol J, Hellings P, Lund V, Fokkens W. Amphotericin B nasal lavages equally as effective as placebo. Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences 2006;31(2):169. [CENTRAL: CN‐00596982; CRS: 1421655]
-
- Ebbens FA, Georgalas C, Luiten S, Drunen CM, Badia L, Scadding GK, et al. The effect of topical amphotericin B on inflammatory markers in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a multicenter randomized controlled study. Laryngoscope 2009;119(2):401‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00681619; CRS: 1486764; PUBMED: 19160404] - PubMed
-
- Ebbens FA, Scadding GK, Badia L, Hellings PW, Jorissen M, Mullol J, et al. Amphotericin B nasal lavages: not a solution for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2006;118(5):1149‐56. [CENTRAL: CN‐00573476; CRS: 1402692; EMBASE: 2006535603; PUBMED: 17088142] - PubMed
Hashemian 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hashemian F, Hashemian F, Molaali N, Rouini M, Roohi E, Torabian S. Clinical effects of topical antifungal therapy in chronic rhinosinusitis: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of intranasal fluconazole. EXCLI Journal. Germany: Leibniz Research Centre for Working Environment and Human Factors (Ardeystr.67, Dortmund D‐44139, Germany. E‐mail: excli@ifado.de), 2016; Vol. 15:95‐102. [CENTRAL: CN‐01138520; CRS: 1869028; EMBASE: 20160151286; PUBMED: 27065776] - PMC - PubMed
-
- IRCT138811063186N1. Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of fluconazol drop on chronic rhinosinusitis [Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of fluconazol drop on chronic rhinosinusitis in patients referred to otorhinolarnyngology clinic in Hamadan]. http://www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=3186&number=1 (first received 2 August 2011). [CENTRAL: CN‐01039355; CRS: 1769954]
Kennedy 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kennedy DW, Kuhn FA, Hamilos DL, Zinreich SJ, Butler D, Warsi G, et al. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with high‐dose oral terbinafine: a double blind, placebo‐controlled study. Laryngoscope 2005;115(10):1793‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00531103; CRS: 1372731; EMBASE: 2005469506; PUBMED: 16222197] - PubMed
Liang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Liang KL, Su MC, Shiao JY, Tseng HC, Hsin CH, Lin JF, et al. Amphotericin B irrigation for the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps: a randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study. American Journal of Rhinology 2008;22(1):52‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00630195; CRS: 1447377; EMBASE: 20083148186; PUBMED: 18284860] - PubMed
Ponikau 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ponikau JU, Sherris DA, Weaver A, Kita H. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with intranasal amphotericin B: a randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind pilot trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2005; Vol. 115, issue 1:125‐31. [CENTRAL: CN‐00502168; CRS: 1346380; EMBASE: 2005024192; PUBMED: 15637558] - PubMed
-
- Sherris DA, Ponikau JU, Weaver A, Frigas E, Kita H. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with intranasal amphotericin B: a prospective, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;113(2 Suppl):2629. [CENTRAL: CN‐00597119; CRS: 1421766] - PubMed
Shin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Shin SH, Ye MK. Effects of topical amphotericin B on expression of cytokines in nasal polyps. Acta Oto‐Laryngologica 2004;124(10):1174‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00505471; CRS: 1349677; PUBMED: 15768813] - PubMed
Weschta 2004 {published data only}
-
- Riechelmann H. Fungus and nasal polyps. 3rd International Consensus Conference on Nasal Polyposis; 2004 Apr 23‐25; Brussels, Belgium. 2004. [CENTRAL: CN‐00519649; CRS: 1362346]
-
- Weschta M, Formanek M, Herbert R. Topical antimycotic treatment after nasal polyps. 106th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO‐HNS). 2002; Vol. 127:P85.
-
- Weschta M, Rimek D, Formanek M, Podbielski A, Riechelmann H. Effect of nasal antifungal therapy on nasal cell activation markers in chronic rhinosinusitis. Archives of Otolaryngology‐‐Head & Neck Surgery 2006;132(7):743‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00566587; CRS: 1395911; PUBMED: 16847182] - PubMed
-
- Weschta M, Rimek D, Formanek M, Polzehl D, Podbielski A, Riechelmann H. Topical antifungal treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a randomized, double‐blind clinical trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2004;113(6):1122‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00467988; CRS: 1317522; PUBMED: 15208594] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Chan 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chan KO, Genoway KA, Javer AR. Effectiveness of itraconazole in the management of refractory allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Journal of Otolaryngology ‐ Head & Neck Surgery 2008;37(6):870‐4. [CRS: 3474502] - PubMed
Gerlinger 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gerlinger I, Fittler A, Fonai F, Patzko A, Mayer A, Botz L. Postoperative application of amphotericin B nasal spray in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, with a review of the antifungal therapy. European Archives of Oto‐rhino‐laryngology 2009;266(6):847‐55. [CENTRAL: CN‐00671532; CRS: 1478049; EMBASE: 20093152029; PUBMED: 18953552] - PubMed
-
- Gerlinger I, Fittler A, Mayer A, Patzko A, Fonay F, Pytel J, et al. Postoperative application of amphotericin B nasal spray in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Can recidive polyposis be prevented? [Amphotericin b‐tartalmu orrspray posztoperativ alkalmazasa orrpolyposissal jaro kronikus rhinosinusitis eseteiben. Megelozheto‐e a recidiva?]. Orvosi Hetilap 2008;149(37):1737‐46. [CENTRAL: CN‐00913521; CRS: 1682078; EMBASE: 2008472251; PUBMED: 18805757] - PubMed
Gupta 2007 {published data only}
Hashemi 2014 {published data only}
Helbling 2006 {published data only}
-
- Helbling A, Baumann A, Hanni C, Caversaccio M. Amphotericin B nasal spray has no effect on nasal polyps. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2006;120(12):1023‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00597184; CRS: 1421814; PUBMED: 16965642] - PubMed
Hofman 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hofman T, Skrobisz W, Hofman A, Hofman M. The estimation of efficacy of fluconazole treatment in patients with chronic sinusitis. Mikologia Lekarska 2004;11(4):297‐301. [CRS: 3474505]
IRCT138706101138N1 {published data only}
-
- IRCT138706101138N1. Effects of intranasal amphotericin‐B irrigation on recurrence of massive nasal polyposis [Effects of intranasal amphotericin‐B irrigation on recurrence of massive nasal polyposis after endoscopic sinus surgery and comparison with nasal corticosteroid sprays]. http://www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=1138&number=1 (first received 30 September 2010). [CENTRAL: CN‐01039346; CRS: 1769945]
Jiang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jiang R‐S, Twu C‐W, Liang K‐L. Effect of 200 mug/ml amphotericin b nasal irrigation on postfunctional endoscopic sinus surgery care. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 2017;157(1 Suppl 1):P159.
-
- Jiang RS, Hsu SH, Liang KL. Amphotericin B nasal irrigation as an adjuvant therapy after functional endoscopic sinus surgery. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy 2015;29(6):435‐40. [CENTRAL: CN‐01134399; CRS: 1864908; EMBASE: 20160037074; PUBMED: 26637583] - PubMed
Joshi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Joshi RR, Bhandary S, Khanal B, Singh RK. Fungal maxillary sinusitis: a prospective study in a tertiary care hospital of eastern Nepal. Kathmandu University Medical Journal (KUMJ) 2007;5(2):195‐8. - PubMed
Khalil 2011 {published data only}
-
- Khalil Y, Tharwat A, Abdou AG, Essa E, Elsawy AH, Elnakib O, et al. The role of antifungal therapy in the prevention of recurrent allergic fungal rhinosinusitis after functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized, controlled study. Ear, Nose, & Throat Journal 2011;90(8):E1‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00804489; CRS: 1600866; EMBASE: 2011499609; PUBMED: 21853425] - PubMed
Lopatin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lopatin AS, Akulich II, Kochetkov PA. Long‐term systemic antifungal therapy for nasal polyposis. European Archives of Oto‐rhino‐laryngology 2007;264(Suppl 1):S282. [CENTRAL: CN‐00596972; CRS: 1421646]
NCT02285283 {published data only}
-
- NCT02285283. RCT of itraconazole for fungal sensitive chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps [Randomized double‐blinded controlled trial of oral antifungal for the treatment of fungal sensitive chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02285283 (first received 6 November 2014). [CENTRAL: CN‐01039767; CRS: 1770363]
Nikakhlagh 2015 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- IRCT201204049375N1. The effect of itraconazole in the treatment of allergic fungal sinusitis [A placebo‐controlled double‐blind randomized trial of itraconazole for allergic fungal sinusitis ‐ allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS)]. http://www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=9375&number=1 (first received 9 April 2013). [CENTRAL: CN‐01012798; CRS: 1743415]
-
- Nikakhlagh S, Khodadadi A, Kanani M, Karampour LS, Saki N. The effect of the oral itraconazole on the management of allergic fungal sinusitis. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal 2015;8:85‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐01138882; CRS: 1869390; EMBASE: 20160128607]
Panda 2012 {published data only}
-
- Panda NK, Francis AA, Chakrabarti A, Virk RS. Oral itraconazole as an adjunct to steroids in AFRS. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 2012;147(2 Suppl):P114. [CENTRAL: CN‐01415741; CRS: 7062506]
Patro 2015 {published data only}
-
- Patro SK, Verma RK, Panda NK, Chakrabarti A, Singh P. Efficacy of preoperative itraconazole in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy 2015;29(4):299‐304. [CENTRAL: CN‐01259222; CRS: 5167418; PUBMED: 26163250] - PubMed
Ravikumar 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ravikumar A, Kumar P. Role of itraconazole in sinonasal polyposis. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 2011;145:127‐8.
Ricchetti 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ricchetti A, Landis BN, Giger R, Aparicio H, Lacroix J‐S. Comparison of the effect of intra‐nasal lavages versus spray with amphotericin B on nasal polyposis. 19th Congress of the European Rhinologic Society; 2002 Jun 16‐19; Ulm, Germany. 2002:152. [CENTRAL: CN‐00404508; CRS: 1265415]
-
- Ricchetti A, Landis BN, Giger R, Zheng C, Lacroix JS. Effect of local antifungal treatment on nasal polyposis. Otorhinolaryngologia Nova 2002;12:48‐51. [CENTRAL: CN‐00452864; CRS: 1305264]
Ricchetti 2002b {published data only}
-
- Ricchetti A, Landis BN, Maffioli A, Giger R, Zeng C, Lacroix JS. Effect of anti‐fungal nasal lavage with amphotericin B on nasal polyposis. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2002;116(4):261‐3. [CRS: 7062668; PUBMED: 11945184] - PubMed
Rojita 2017 {published data only}
Somu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Somu L, Saravanam PK, Ravikumar. Role of itraconazole in sino nasal polyposis. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2015;4(70):12112‐9. [CRS: 7062671]
Thamboo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Thamboo A, Thamboo A, Philpott C, Javer A, Clark A. Single‐blind study of manuka honey in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Journal d'Oto‐rhino‐laryngologie et de Chirurgie Cervico‐faciale 2011;40(3):238‐43. [CENTRAL: CN‐00795839; CRS: 1592410; PUBMED: 21518647] - PubMed
Verma 2016 {published data only}
-
- Verma RK, Patro SK, Francis AA, Panda NK, Chakrabarti A, Singh P. Role of preoperative versus postoperative itraconazole in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Medical Mycology 2016;6:614‐23. - PubMed
Zhang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhang Z, Zhang J, Luo W, Jiang H. Surgery added with fluconazole in treatment of fungal rhinosinusitis. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke za Zhi [Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery] 2012;26(15):692‐3, 696. [CENTRAL: CN‐00850362; CRS: 1626206; PUBMED: 23167181] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Deka 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Deka RC, Chokkalingam V, Vishnoi RK, Kumar R. Topical amphotericin B and steroid in AFS. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 2007;137(2 Suppl 1):40. [CENTRAL: CN‐00614784; CRS: 1435672]
Frigas 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Frigas E. A pilot, prospective, double blind, placebo‐controlled treatment trial with itraconazole orally in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2007;119(1):560. [CENTRAL: CN‐00725113; CRS: 1526958]
Lopatin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lopatin AS, Akulich II, Kochetkov PA. Systemic antifungals in the treatment of nasal polyposis: do they work?. 3rd International Consensus Conference on Nasal Polyposis; 2004 Apr 23‐25; Brussels, Belgium. 2004. [CENTRAL: CN‐00519616; CRS: 1362322]
Stergiou 2007 {published data only}
-
- NCT00425620. Amphotericin B suspension in refractory chronic sinusitis [A prospective, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicenter, parallel‐group study of intranasal amphotericin B suspension in patients with refractory, postsurgical chronic sinusitis (CS)]. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/nct00425620 (first received 23 January 2007). [CENTRAL: CN‐00861830; CRS: 1636508]
-
- Stergiou A, Casciano R, Katz L, Etschmaier M, Sherris D, Tichenor W, et al. Intranasal amphotericin B in patients with refractory, postsurgical chronic sinusitis: a phase III pivotal clinical trial design. XXVI Congress of the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (EAACI); 2007 Jun 9‐13; Goteburg, Sweden. 2007:Abstract No. 45. [CENTRAL: CN‐00597001; CRS: 1421672]
Additional references
Balk 2012
-
- Balk EM, Earley A, Patel K, Trikalinos TA, Dahabreh IJ. Empirical Assessment of Within‐arm Correlation Imputation in Trials of Continuous Outcomes [Internet]. Report No.: 12(13)‐EHC141‐EF. AHRQ Methods for Effective Health Care. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2012. - PubMed
Bent 1994
-
- Bent JP 3rd, Kuhn FA. Diagnosis of allergic fungal sinusitis. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1994;111(5):580‐5. - PubMed
BNF 2018
-
- Joint Formulary Committee. British National Formulary (online). London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press (http://www.medicinescomplete.com) (accessed 23 May 2018).
Braun 2003
-
- Braun H, Buzina W, Freudenschuss K, Beham A, Stammberger H. Eosinophilic fungal rhinosinusitis: a common disorder in Europe?. Laryngoscope 2003;113(2):264‐9. - PubMed
Chakrabarti 2009
Chen 2003
-
- Chen Y, Dales R, Lin M. The epidemiology of chronic rhinosinusitis in Canadians. Laryngoscope 2003;113(7):1199‐205. - PubMed
Cho 2012
Chong 2016a
Chong 2016b
Chong 2016c
CHROME 2017
-
- Hopkins C, Hettige R, Soni‐Jaiswal A, Lakhani R, Carrie S, Cervin A, et al. CHronic Rhinosinusitis Outcome MEasures (CHROME) – developing a core outcome set for trials of interventions in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 2018;56(1):22‐32. - PubMed
DeMarcantonio 2011
-
- DeMarcantonio MA, Han JK. Nasal polyps: pathogenesis and treatment implications. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America 2011;44(3):685‐95, ix. - PubMed
Ebbens 2007
-
- Ebbens FA, Georgalas C, Rinia AB, Drunen CM, Lund VJ, Fokkens WJ. The fungal debate: where do we stand today?. Rhinology 2007;45(3):178‐89. - PubMed
Ebbens 2010
-
- Ebbens FA, Toppila‐Salmi SK, Renkonen JA, Renkonen RL, Mullol J, Drunen CM, et al. Endothelial L‐selectin ligand expression in nasal polyps. Allergy 2010;65(1):95‐102. - PubMed
Ebbens 2011
-
- Ebbens FA, Toppila‐Salmi S, Groot EJ, Renkonen J, Renkonen R, Drunen CM, et al. Predictors of post‐operative response to treatment: a double blind placebo controlled study in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Rhinology 2011;49(4):413‐9. - PubMed
Egger 1997
EPOS 2012
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology. Supplement 2012;50 Suppl 23:1‐298. - PubMed
Erskine 2015
-
- Erskine SE, Verkerk MM, Notley C, Williamson IG, Philpott, CM. Chronic rhinosinusitis: patient experiences of primary and secondary care – a qualitative study. Clinical Otolaryngology 2015;41:8‐14. - PubMed
Fokkens 2007
-
- Fokkens W, Lund V, Mullol J. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2007. Rhinology 2007;45(Suppl 20):1‐139. - PubMed
Gliklich 1995
-
- Gliklich RE, Metson R. The health impact of chronic sinusitis in patients seeking otolaryngologic care. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1995;113(1):104‐9. - PubMed
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hastan 2011
-
- Hastan D, Fokkens WJ, Bachert C, Newson RB, Bislimovska J, Bockelbrink A, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe ‐ an underestimated disease. A GA2LEN study. Allergy 2011;66(9):1216‐23. - PubMed
Head 2016a
Head 2016b
Head 2016c
Juniper 1991
-
- Juniper EF, Guyatt GH. Development and testing of a new measure of health status for clinical trials in rhinoconjunctivitis. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 1991;21:77‐83. - PubMed
Kern 2008
Keswani 2012
Lackner 2005
-
- Lackner A, Stammberger H, Buzina W, Freudenschuss K, Panzitt T, Schosteritsch S, et al. Fungi: a normal content of human nasal mucus. American Journal of Rhinology 2005;19(2):125‐9. - PubMed
Larsen 2004
-
- Larsen P, Tos M. Origin of nasal polyps: an endoscopic autopsy study. Laryngoscope 2004;114(4):710‐9. - PubMed
Mistry 2014
-
- Mistry SG, Kumar BN. The value of antifungal therapy in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 2014;52(1):9‐18. - PubMed
Philpott 2011
-
- Philpott CM, Clark A, Javer AR. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis ‐ a new staging system. Rhinology 2011;49:318‐23. - PubMed
Ponikau 1999
-
- Ponikau JU, Sherris DA, Kern EB, Homburger HA, Frigas E, Gaffey TA, et al. The diagnosis and incidence of allergic fungal sinusitis. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 1999;74(9):877‐84. - PubMed
Ponikau 2007
-
- Ponikau JU, Sherris DA, Kita H. The role of ubiquitous airborne fungi in chronic rhinosinusitis. Clinical Allergy and Immunology 2007;20:177‐84. - PubMed
Ragab 2004
-
- Ragab SM, Lund VJ, Scadding G. Evaluation of the medical and surgical treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis: a prospective, randomised, controlled trial. Laryngoscope 2004;114(5):923‐30. - PubMed
Ragab 2010
-
- Ragab SM, Lund VJ, Scadding G, Saleh HA, Khalifa MA. Impact of chronic rhinosinusitis therapy on quality of life: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Rhinology 2010;48(3):305‐11. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Sok 2006
-
- Sok JC, Ferguson BJ. Differential diagnosis of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports 2006;6:203‐14. - PubMed
Tan 2011
Tomassen 2011
-
- Tomassen P, Zele T, Zhang N, Perez‐ Novo C, Bruaene N, Gevaert P, et al. Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 2011;8(1):115‐20. - PubMed
van Drunen 2009
-
- Drunen CM, Reinartz SM, Wigman J, Fokkens W. Inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. Immunology and Allergy Clinics of North America 2009;29(4):621‐9. - PubMed
Wild 2005
-
- Wild D, Grove A, Martin M, Eremenco S, McElroy S, Verjee‐Lorenz A, et al. Principles of good practice for the translation and cultural adaptation process for patient‐reported outcomes (PRO) measures: report of the ISPOR Task Force for Translation and Cultural Adaptation. Value in Health 2005;8(2):94‐104. - PubMed
Yousefi 2017
-
- Yousefi J, Akhavan A, Hoseini‐Motlagh R, Banaei‐Boroujeni S, Panahi Y, Hossein Khosravi M. Effect of amphotericin B on treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis: a double‐blind randomized clinical trial. Razavi International Journal of Medicine 2017;5(4):e64550.
Zhang 2008
-
- Zhang N, Zele T, Perez‐Novo C, Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, et al. Different types of T‐effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2008;122(5):961‐8. - PubMed
Zhang 2009
-
- Zhang XH, Lu X, Long XB, You XJ, Gao QX, Cui YH, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps is associated with decreased expression of glucocorticoid‐induced leucine zipper. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 2009;39(5):647‐54. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

