Effect of educational interventions on health in childhood: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 30200070
- PMCID: PMC6133573
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011849
Effect of educational interventions on health in childhood: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Retraction in
-
Effect of educational interventions on health in childhood: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials: Retraction.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Aug 20;100(33):e27006. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027006. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34414991 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
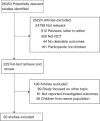
Background: The purpose of this study was to summarize the evidences from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the effects of educational interventions in overweight/obesity childhood by using meta-analytic approach.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library databases were searched from the inception to April 2018. Weighted mean differences (WMDs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to measure the effects of educational interventions during childhood in the random-effects models.
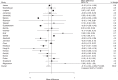
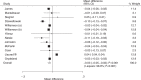
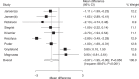
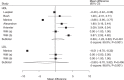
Results: Thirty RCTs reporting data on 35,296 children were included in the meta-analysis. The summary WMD indicated that children received educational interventions had lower levels of body mass index (BMI) (WMD: -0.15; 95% CI: -0.24 to -0.05; P = .003), BMI z-score (WMD: -0.03; 95% CI: -0.05 to -0.02; P < .001), waist circumference (WMD: -0.97; 95% CI: -1.95 to -0.00; P = 0.050), triceps skinfold (WMD: -1.39; 95% CI: -2.41 to -0.37; P = .008), systolic blood pressure (WMD: -1.13; 95% CI: -2.20 to -0.07; P = .037), total cholesterol (WMD: -4.04; 95% CI: -7.18 to -0.90; P = .012), and triglyceride (WMD: -2.62; 95% CI: -4.33 to -0.90; P = .003). However, educational interventions were not associated with the levels of waist-to-hip ratio, diastolic blood pressure, high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein.
Conclusion: The study findings elucidate the positive effects of educational interventions on BMI, BMI z-score, waist circumference, triceps skinfold, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, and triglyceride.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of multiple eHealth-delivered lifestyle strategies for preventing or intervening overweight/obesity among children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 5;13:999702. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.999702. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36157474 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture and related techniques for obesity and cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis.Acupunct Med. 2020 Aug;38(4):227-234. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2018-011646. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Acupunct Med. 2020. PMID: 32310001
-
Effectiveness of dietary interventions on weight outcomes in childhood: a systematic review meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Apr;10(4):701-714. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-183. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34012820 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Epidemic Intermittent Fasting on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Nutr. 2021 Oct 18;8:669325. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.669325. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34733872 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of l-carnitine supplementation for weight management in overweight and obese adults: An updated systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jan;151:104554. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104554. Epub 2019 Nov 17. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 31743774
Cited by
-
Influence of pilot and small trials in meta-analyses of behavioral interventions: a meta-epidemiological study.Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 18;12(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02184-7. Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36803891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of educational interventions on health in childhood: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials: Retraction.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Aug 20;100(33):e27006. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027006. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34414991 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lobstein T, Bauer L, Uauy R. IASO International Obesity Task Force. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes Rev 2004;5(Suppl. 1):1–04. - PubMed
-
- Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Boyce WF, et al. . Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children Obesity Working Group. Comparison of overweight and obesity prevalence in school-aged youth from 34 countries and their relationships with physical activity and dietary patterns. Obes Rev 2005;6:123–32. - PubMed
-
- Flynn MA, McNeil DA, Maloff B, et al. . Reducing obesity and related chronic disease risk in children and youth: a synthesis of evidence with ‘best practice’ recommendations. Obes Rev 2006;7(Suppl 1):7–66. - PubMed
-
- Bray GA, Gray DS. Treatment of obesity: an overview. Diabetes Metab Rev 2010;4:653–79. - PubMed
-
- National Task Force on the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity. Overweight, obesity, and health risk. Arch Intern Med 2000;160:898–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

