Comparison and correlation between the pediatric Voice Handicap Index and the pediatric voice-related quality-of-life questionnaires
- PMID: 30200071
- PMCID: PMC6133469
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011850
Comparison and correlation between the pediatric Voice Handicap Index and the pediatric voice-related quality-of-life questionnaires
Abstract
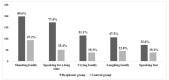
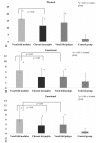
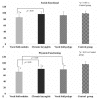
The aim of this study was to investigate differences and correlations between the pediatric Voice Handicap Index (pVHI) and the pediatric Voice-Related Quality-of-life (pVRQOL) questionnaires in children with and without voice disorders. This was a cross-sectional study.A total of 418 parents with children aged 2 to 14 years participated in this study from May 2016 to July 2017. This included 221 parents of children with voice disorders (dysphonic group) and 197 parents of children without voice disorders (control group). The scores for the pVHI and the pVRQOL were compared, and correlation analysis was performed.Compared with the control group, the dysphonic group had a significantly higher total score and subscale scores for the pVHI (P < .001), and significantly lower pVRQOL scores (P < .001). The pVHI showed greater differences in subscale scores among the three dysphonic subgroups than the pVRQOL. The Spearman correlation coefficient between the pVHI and pVRQOL was -0.844 (P < .001). The total scores for the pVHI and pVRQOL also correlated significantly for each diagnostic category (P < .001).Voice-related quality of life was poorer in children with voice disorders than in those without voice disorders. The pVHI and pVRQOL scores were moderately- to strongly correlated. These may be useful tools for assessing the voice-related quality of life in children. The pVHI may provide more useful details about the effects of different types of voice disorders on the voice-related quality of life than the pVRQOL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of pediatric voice handicap index and pediatric voice related quality of life before and after adenotonsillectomy in pediatric population.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Mar;79(3):388-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.12.034. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25599861
-
Health-related quality of life in children with dysphonia and validation of the French Pediatric Voice Handicap Index.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jan;104:205-209. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.09.026. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29287869
-
The Arabic translation, cultural adaptation, and validation of the pediatric voice-related quality of life survey.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Jan;116:30-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.10.018. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30554703
-
Adaptation and Validation of the Mandarin Chinese Version of the Pediatric Voice Handicap Index-10 (pVHI-10).J Voice. 2024 Jan;38(1):243.e31-243.e35. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2021.07.021. Epub 2021 Aug 30. J Voice. 2024. PMID: 34470707
-
A Meta-Analytic Reliability Generalization Study of the Pediatric Voice Handicap Index.J Voice. 2024 Aug 22:S0892-1997(24)00221-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2024.07.013. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2024. PMID: 39179469 Review.
Cited by
-
The Pediatric Vocal Mechanism: Structure and Function.J Voice. 2025 Apr 4:S0892-1997(25)00118-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2025.03.025. Online ahead of print. J Voice. 2025. PMID: 40187973 Review.
-
Dysphonia in Children; Clinical Profile, Conservative Treatment Modalities and Outcomes: An Institutional Experience.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Dec;75(4):3248-3255. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-03952-6. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023. PMID: 37974702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roy N, Merrill RM, Thibeault S, et al. Prevalence of voice disorders in teachers and the general population. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2004;47:281–93. - PubMed
-
- Seifpanahi S, Izadi F, Jamshidi AA, et al. Prevalence of voice disorders and associated risk factors in teachers and nonteachers in Iran. J Voice 2016;30:506e519-523. - PubMed
-
- Connor NP, Cohen SB, Theis SM, et al. Attitudes of children with dysphonia. J Voice 2008;22:197–209. - PubMed
-
- Akif Kilic M, Okur E, Yildirim I, et al. The prevalence of vocal fold nodules in school age children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2004;68:409–12. - PubMed
-
- Romak JJ, Orbelo DM, Maragos NE, et al. Correlation of the Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10) and Voice-Related Quality of Life (V-RQOL) in patients with dysphonia. J Voice 2014;28:237–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

