Preoperative oral thyroid hormones to prevent euthyroid sick syndrome and attenuate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass in children: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 30200092
- PMCID: PMC6133632
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012100
Preoperative oral thyroid hormones to prevent euthyroid sick syndrome and attenuate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass in children: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Both euthyroid sick syndrome and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury are common and have been significantly associated with morbidity and mortality after pediatric cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. This single-center, prospective, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled clinical pilot trial was designed to assess if preoperative oral thyroid hormone therapy could prevent the occurrence of euthyroid sick syndrome (ESS) and attenuate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) in children.
Methods: Forty children aged 3 to 12 year, scheduled for elective congenital heart disease repair surgery with CPB, were randomized into 2 groups of equal size to receive the following treatments in a double-blind manner: placebo (control group) and thyroid tablet 0.4 mg/kg (trial group) taken orally once a day for 4 days before surgery. The perioperative serum thyroid hormone levels and hemodynamic variables were determined. The extubation time, duration of intensive care unit (ICU) stay, and use of inotropic drugs in the ICU were recorded. The myocardial expressions of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), myosin heavy chain (MHC) mRNA, and thyroid hormone receptor (TR) mRNA were detected. The serum creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) activity and troponin I (TnI) positive ratio at 24 hour after surgery were assessed.
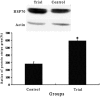
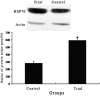
Results: There were no significant differences in hemodynamic variables at all observed points, extubation time, and duration of ICU stay between groups. As compared with baselines on administration, serum triiodothyronine (T3) and free T3 (FT3) levels on the first, second, and fourth postoperative day, and serum thyrotropic-stimulating hormone (TSH), tetraiodothyronine (T4), and free T4 (FT4) levels on the first postoperative day were significantly decreased in the 2 groups. Serum T3, FT3, and T4 levels on the first and second postoperative day, and serum FT4 level on the first postoperative day were significantly higher in the trial group than in control group. As compared with the control group, the number of patients requiring inotropic drugs in the ICU, serum CK-MB activity, serum positive TnI ratio, and myocardial expression of MHCβ mRNA were significantly decreased, and myocardial expressions of both HSP70 and MHCα mRNA were significantly increased in the trial group.
Conclusions: In children undergoing cardiac surgery with CPB, preoperative oral small-dose thyroid hormone therapy reduces severity of postoperative ESS and provides a protection against myocardial IRI by increasing HSP70 and MHCα expression.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no financial support and potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Gerdes AM, Ojamaa K. Thyroid hormone and cardioprotection. Compr Physiol 2016;6:1199–219. - PubMed
-
- Pantos C, Mourouzis I. Translating thyroid hormone effects into clinical practice: the relevance of thyroid hormone receptor α1 in cardiac repair. Heart Fail Rev 2015;20:273–82. - PubMed
-
- Talwar S, Khadgawat R, Sandeep JA, et al. Cardiopulmonary bypass and serum thyroid hormone profile in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis 2012;7:433–40. - PubMed
-
- Bettendorf M, Schmidt KG, Grulich-Henn J, et al. Tri-iodothyronine treatment in children after cardiac surgery: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2000;356:529–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous