Causes and prognosis of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in 48 subjects: A 10-year retrospective case series
- PMID: 30200110
- PMCID: PMC6133590
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012150
Causes and prognosis of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in 48 subjects: A 10-year retrospective case series
Abstract
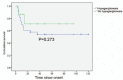
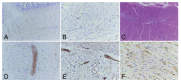
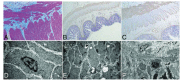
The aim of the study was to evaluate the prognosis and survival of pediatric subjects with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) and investigate the independent risk factors affecting their prognosis.This was a retrospective case series of all pediatric subjects suffering from CIPO and treated at the Pediatric Surgical ward of Xinhua Hospital between January 2006 and January 2016.The overall mortality was 19/48 (39.6%). Because of delayed CIPO diagnosis, many subjects underwent a variety of surgical procedures. The rate of additional surgical procedures was high (35/48, 72.9%), but the number of surgical procedures, parenteral nutrition, and megacystis did not affect mortality. Mycotic infection was significantly associated with mortality, while onset at <1 year and hypoganglionosis showed a tendency to be associated with mortality.Mycotic infection was associated with mortality of children with CIPO. Despite improving treatment approaches, the overall prognosis of CIPO remains poor. The choice of the surgical intervention could be based on standard criteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term outcome of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction adult patients requiring home parenteral nutrition.Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 May;104(5):1262-70. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.58. Epub 2009 Apr 14. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19367271
-
Frequency of mitochondrial defects in patients with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction.Gastroenterology. 2009 Jul;137(1):101-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.03.054. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19344718
-
Surgical treatment and prognosis of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in children.J Pediatr Surg. 2005 Nov;40(11):1753-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.07.046. J Pediatr Surg. 2005. PMID: 16291165
-
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction due to adult-onset acquired isolated hypoganglionosis with muscular atrophy in the small intestine: a case report and review of literature.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr;17(2):244-252. doi: 10.1007/s12328-023-01902-x. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38193986 Review.
-
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;21(4):657-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2007.03.002. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17643907 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Case of Chronic Small Bowel Pseudo-Obstruction.Cureus. 2020 May 7;12(5):e8003. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8003. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32528745 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, diagnostics, therapeutic management and outcomes of paediatric intestinal pseudo-obstruction in the Netherlands: A 20-year retrospective cohort study.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025 Jan;80(1):34-45. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12400. Epub 2024 Nov 1. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39487095 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic integration of enteric neural stem cells in ex vivo organotypic colon cultures.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 5;11(1):15889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95434-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34354183 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Presentation of a Pediatric Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction Episode After SARS-CoV-2 Virus (COVID-19) Infection.JPGN Rep. 2021 Apr 12;2(2):e059. doi: 10.1097/PG9.0000000000000059. eCollection 2021 May. JPGN Rep. 2021. PMID: 34192292 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical Outcomes of Pediatric Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction.J Clin Med. 2021 May 28;10(11):2376. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112376. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34071279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudolph CD, Hyman PE, Altschuler SM, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in children: report of consensus workshop. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1997;24:102–12. - PubMed
-
- Lindberg G, Tornblom H, Iwarzon M, et al. Full-thickness biopsy findings in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction and enteric dysmotility. Gut 2009;58:1084–90. - PubMed
-
- Vargas JH, Sachs P, Ament ME. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in pediatrics. Results of a national survey by members of the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1988;7:323–32. - PubMed
-
- Muto M, Matsufuji H, Tomomasa T, et al. Pediatric chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a rare, serious, and intractable disease: a report of a nationwide survey in Japan. J Pediatr Surg 2014;49:1799–803. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

