Investigation of Novel Pesticides with Insecticidal and Antifungal Activities: Design, Synthesis and SAR Studies of Benzoylpyrimidinylurea Derivatives
- PMID: 30200298
- PMCID: PMC6225173
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23092203
Investigation of Novel Pesticides with Insecticidal and Antifungal Activities: Design, Synthesis and SAR Studies of Benzoylpyrimidinylurea Derivatives
Abstract
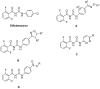
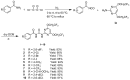
In order to find pesticides with insecticidal and antifungal activities, a series of novel benzoyl pyrimidinylurea derivatives were designed and synthesized. All target compounds were identified by ¹H-NMR spectroscopy and HRMS. Insecticidal and antifungal activity of these compounds were evaluated and the structure-activity relationships (SAR) were clearly and comprehensively illustrated. Compound 7, with low toxicity to zebrafish (LC50 = 378.387 µg mL-1) showed 100% inhibition against mosquito (Culex pipiens pallens) at 0.25 µg mL-1. Both compounds 19 and 25 exhibited broad-spectrum fungicidal activity (>50% inhibitory activities against 13 phytopathogenic fungi), which were better than those of the commercial pesticide pyrimethanil (>50% inhibitory activities against eight phytopathogenic fungi). Furthermore, compounds 19 and 25 exhibited protective activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on leaves of Brassica oleracea L. during in vivo experiments.
Keywords: antifungal activity; benzoylpyrimidinylurea derivatives; embryo toxicity; insecticidal activity; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Ishaaya I., Degheele D. Insecticides with Novel Modes of Action: Mechanisms and Application. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1998. p. 289.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

