Transient Receptor Potential Channel A1 (TRPA1) Regulates Sulfur Mustard-Induced Expression of Heat Shock 70 kDa Protein 6 (HSPA6) In Vitro
- PMID: 30200301
- PMCID: PMC6162519
- DOI: 10.3390/cells7090126
Transient Receptor Potential Channel A1 (TRPA1) Regulates Sulfur Mustard-Induced Expression of Heat Shock 70 kDa Protein 6 (HSPA6) In Vitro
Abstract
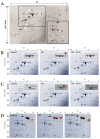
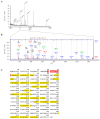
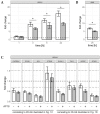
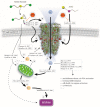
The chemosensory transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) ion channel perceives different sensory stimuli. It also interacts with reactive exogenous compounds including the chemical warfare agent sulfur mustard (SM). Activation of TRPA1 by SM results in elevation of intracellular calcium levels but the cellular consequences are not understood so far. In the present study we analyzed SM-induced and TRPA1-mediated effects in human TRPA1-overexpressing HEK cells (HEKA1) and human lung epithelial cells (A549) that endogenously exhibit TRPA1. The specific TRPA1 inhibitor AP18 was used to distinguish between SM-induced and TRPA1-mediated or TRPA1-independent effects. Cells were exposed to 600 µM SM and proteome changes were investigated 24 h afterwards by 2D gel electrophoresis. Protein spots with differential staining levels were analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and nano liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Results were verified by RT-qPCR experiments in both HEKA1 or A549 cells. Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6 (HSPA6) was identified as an SM-induced and TRPA1-mediated protein. AP18 pre-treatment diminished the up-regulation. RT-qPCR measurements verified these results and further revealed a time-dependent regulation. Our results demonstrate that SM-mediated activation of TRPA1 influences the protein expression and confirm the important role of TRPA1 ion channels in the molecular toxicology of SM.
Keywords: 2D gel electrophoresis; AP18; HEK293; HSP70; MALDI-TOF MS(/MS); TRPA1; nanoHPLC-ESI MS/MS; proteomics; sulfur mustard.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the chemosensing transient receptor potential channel A1 (TRPA1) by alkylating agents.Arch Toxicol. 2015 Sep;89(9):1631-43. doi: 10.1007/s00204-014-1414-4. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Arch Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25395009
-
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine inhibits sulfur mustard-induced and TRPA1-dependent calcium influx.Arch Toxicol. 2017 May;91(5):2179-2189. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1873-x. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27738742
-
Sulfur mustard induced nuclear translocation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase (GAPDH).Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Dec 5;206(3):529-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23827652
-
Mass spectrometric analysis of sulfur mustard-induced biomolecular adducts: Are DNA adducts suitable biomarkers of exposure?Toxicol Lett. 2018 Sep 1;293:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Toxicol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29277573 Review.
-
Surface analysis of lipids by mass spectrometry: more than just imaging.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):329-53. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23623802 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels in Health and Disease.Cells. 2019 May 4;8(5):413. doi: 10.3390/cells8050413. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31060230 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin as Modulator for Sulfur and Nitrogen Mustard-Induced Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage: Molecular Therapeutics.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 6;12(2):397. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020397. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steinritz D., Balszuweit F., Thiermann H., Kehe K. Mustard: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Approaches. In: Worek F., Jenner J., Thiermann H., editors. Chemical Warfare Toxicology. Royal Society of Chemistry; Cambridge, UK: 2016. pp. 120–156.
-
- Kehe K., Steinritz D., Balszuweit F., Thiermann H. Long-Term Effects of the Chemical Warfare Agent Sulfur Mustard. In: Worek F., Jenner J., Thiermann H., editors. Chemical Warfare Toxicology. Royal Society of Chemistry; Cambridge, UK: 2016. pp. 179–190.
-
- Steinritz D., Thiermann H. Sulfur Mustard. In: Brent J., Burkhart K., Dargan P.I., Hatten B., Megarbane B., Palmer R., White J., editors. Critical Care Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Critically Poisoned Patient. 2nd ed. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. pp. 2683–2712.
-
- Stenger B., Zehfuss F., Mückter H., Schmidt A., Balszuweit F., Schäfer E., Büch T., Gudermann T., Thiermann H., Steinritz D. Activation of the chemosensing transient receptor potential channel A1 (TRPA1) by alkylating agents. Arch. Toxicol. 2015;89:1631–1643. doi: 10.1007/s00204-014-1414-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

