Royal Jelly Delays Motor Functional Impairment During Aging in Genetically Heterogeneous Male Mice
- PMID: 30200401
- PMCID: PMC6164577
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10091191
Royal Jelly Delays Motor Functional Impairment During Aging in Genetically Heterogeneous Male Mice
Abstract
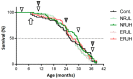
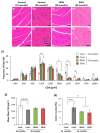
Aging is associated with motor disorders that decrease the quality of life (QOL). Royal jelly (RJ), used as a dietary supplement, has shown various health benefits and, therefore, it has the potential to improve the QOL during aging. We have previously developed protease enzyme-treated RJ to avoid the anaphylactic response induced by RJ supplementation. However, the effects of a lifelong treatment with RJ on normal aging have not been fully clarified. In this study, we investigated the effects of enzyme-untreated RJ (NRJ) and enzyme-treated RJ (ERJ) on the aging process focusing on motor functions, by using a genetically heterogeneous (HET) mouse model experimentally endowed with genetic diversity. We performed four different physical performance tests (grip strength, wire hang, horizontal bar, and rotarod). We showed that the age-related impairment of the motor functions was significantly delayed in RJ-treated mice. Both NRJ and ERJ were similarly effective against these types of aging-associated declines. Histological analyses revealed that the RJ treatment affected the muscle fiber size at an advanced age. We also demonstrated that age-related changes in muscle satellite cell markers and catabolic genes were affected in RJ-treated mice. These results suggest that non-protein components of RJ improved the motor function in aging mice. These findings indicate that RJ has the potential to change the QOL during aging by regulating the motor function.
Keywords: aging; genetically heterogeneous mice; motor function; muscle atrophy; muscle stemness; royal jelly.
Conflict of interest statement
N.O., T.I., T.T., and K.H. are employees of Yamada Bee Company, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Royal jelly prevents the progression of sarcopenia in aged mice in vivo and in vitro.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013 Dec;68(12):1482-92. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt041. Epub 2013 May 8. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23657970
-
Daily Oral Administration of Protease-Treated Royal Jelly Protects Against Denervation-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy.Nutrients. 2020 Oct 11;12(10):3089. doi: 10.3390/nu12103089. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33050588 Free PMC article.
-
Royal Jelly-Mediated Prolongevity and Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans Is Possibly Modulated by the Interplays of DAF-16, SIR-2.1, HCF-1, and 14-3-3 Proteins.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015 Jul;70(7):827-38. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu120. Epub 2014 Jul 29. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25073462
-
Royal Jelly and Its Components Promote Healthy Aging and Longevity: From Animal Models to Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 20;20(19):4662. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194662. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31547049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creatine supplementation: can it improve quality of life in the elderly without associated resistance training?Curr Aging Sci. 2013 Dec;6(3):251-7. doi: 10.2174/1874609806666131204153102. Curr Aging Sci. 2013. PMID: 24304199 Review.
Cited by
-
Royal Jelly Supplementation Improves Endurance and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Athletes: A Crossover Trial.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 16;13(7):e70497. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70497. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40678328 Free PMC article.
-
Royal Jelly-A Traditional and Natural Remedy for Postmenopausal Symptoms and Aging-Related Pathologies.Molecules. 2020 Jul 20;25(14):3291. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143291. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32698461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Royal Jelly Increases Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Peripheral Blood: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial in Healthy Subjects.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jan 13;2023:7665515. doi: 10.1155/2023/7665515. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36686976 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Compounds Attenuate Denervation-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 2;22(15):8310. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158310. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health Promoting Properties of Bee Royal Jelly: Food of the Queens.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 7;13(2):543. doi: 10.3390/nu13020543. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33562330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Luca d’Alessandro E., Bonacci S., Giraldi G. Aging populations: The health and quality of life of the elderly. Clin. Ter. 2011;162:e13–e18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

