Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Fatty Acids Extracted from Halocynthia aurantium Tunic in RAW264.7 Cells
- PMID: 30200438
- PMCID: PMC6163248
- DOI: 10.3390/md16090309
Immune-Enhancement and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Fatty Acids Extracted from Halocynthia aurantium Tunic in RAW264.7 Cells
Abstract
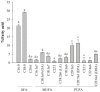
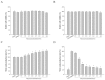
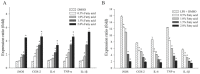
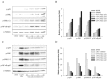
Halocynthia aurantium, an edible ascidian species, has not been studied scientifically, even though tunicates and ascidians are well-known to contain several unique and biologically active materials. The current study investigated the fatty acid profiles of the H. aurantium tunic and its immune-regulatory effects on RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Results of the fatty acid profile analysis showed a difference in ratios, depending on the fatty acids being analysed, including those of saturated fatty acids (SFA), monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). In particular, omega-3 fatty acids, such as eicosatrienoic acid n-3 (ETA n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), were much higher than omega-6 fatty acids. Moreover, the H. aurantium tunic fatty acids, significantly and dose-dependently, increased the NO and prostaglandin E2 (PGE₂) production in RAW264.7 cells, for immune-enhancement without cytotoxicity. In addition, these fatty acids regulated the transcription of immune-associated genes, including iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, and TNF-α. These actions were activated and deactivated via Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)and NF-κB signaling, to regulate the immune responses. Conversely, the H. aurantium tunic fatty acids effectively suppressed the inflammatory cytokine expressions, including iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, and TNF-α, in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Productions of COX-2 and PGE₂, which are key biomarkers for inflammation, were also significantly reduced. These results elucidated the immune-enhancement and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the H. aurantium tunic fatty acids in macrophage cells. Moreover, the H. aurantium tunic might be a potential fatty acid source for immune-modulation.
Keywords: Halocynthia aurantium; MAPK; NF-κB pathway; fatty acids; immunomodulation; tunic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

