Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice
- PMID: 30200495
- PMCID: PMC6163254
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10091208
Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice
Abstract
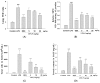
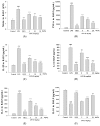
The anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside Rh2 (GRh2) has labeled it as one of the most important ginsenosides. The purpose of this study was to identify the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of GRh2 using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge lung-injury animal model. GRh2 reduced LPS-induced proinflammatory mediator nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1β, and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10) production in lung tissues. GRh2 treatment decreased the histological alterations in the lung tissues and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) protein content; total cell number also reduced in LPS-induced lung injury in mice. Moreover, GRh2 blocked iNOS, COX-2, the phosphorylation of IκB-α, ERK, JNK, p38, Raf-1, and MEK protein expression, which corresponds with the growth of HO-1, Nrf-2, catalase, SOD, and GPx expression in LPS-induced lung injury. An in vivo experimental study suggested that GRh2 has anti-inflammatory effects, and has potential therapeutic efficacy in major anterior segment lung diseases.
Keywords: MEK; Nrf-2; acute lung injury; ginsenoside Rh2; lipopolysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest with respect to the data collected and procedures used within this study.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Attenuation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Hispolon in Mice, Through Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways, and Suppressing Oxidative Stress-Mediated ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 10;12(6):1742. doi: 10.3390/nu12061742. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32532087 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jul;28(13):e18386. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18386. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38990057 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Sanghuangporus sanghuang Mycelium.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 7;18(2):347. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020347. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28178212 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential and Mechanisms of Novel Simple O-Substituted Isoflavones against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10394. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810394. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer effects and potential mechanisms of ginsenoside Rh2 in various cancer types (Review).Oncol Rep. 2021 Apr;45(4):33. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7984. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649861 Review.
Cited by
-
Hesperetin, a Citrus Flavonoid, Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis and Memory Impairments by Modulating TLR4/NF-κB Signaling.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 17;11(3):648. doi: 10.3390/nu11030648. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30884890 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Pharmacology and Verification of ShenFuHuang Formula in Zebrafish Model Reveal Multi-Scale Treatment Strategy for Septic Syndrome in COVID-19.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;11:584057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584057. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33041827 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway and silicosis.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 May 7;10(3):487-494. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa109. eCollection 2021 May. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34141162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects and mechanisms of a biosynthetic ginsenoside 3β,12β-Di-O-Glc-PPD on non-small cell lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Sep 9;12:7375-7385. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S217039. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31571900 Free PMC article.
-
American Ginseng Attenuates Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage via the Modulation of Lipid Peroxidation and Inflammatory Adaptation in Males.Nutrients. 2021 Dec 25;14(1):78. doi: 10.3390/nu14010078. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 35010953 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Li K.C., Ho Y.L., Hsieh W.T., Huang S.S., Chang Y.S., Huang G.J. Apigenin-7-glycoside prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury via downregulation of oxidative enzyme expression and protein activation through inhibition of MAPK phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015;16:1736–1754. doi: 10.3390/ijms16011736. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang G.J., Deng J.S., Chen C.C., Huang C.J., Sung P.J., Huang S.S., Kuo Y.H. Methanol extract of Antrodia camphorata protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014;62:5321–5329. doi: 10.1021/jf405113g. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang J.S., Lin H.J., Deng J.S., Wu W.T., Huang S.S., Huang G.J. Preventive effects of Velvet Antler (Cervus elaphus) against lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB activation and inducing AMPK/Nrf2 pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018;2018:2870503. doi: 10.1155/2018/2870503. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

