The Na/K-ATPase Signaling: From Specific Ligands to General Reactive Oxygen Species
- PMID: 30200500
- PMCID: PMC6163532
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092600
The Na/K-ATPase Signaling: From Specific Ligands to General Reactive Oxygen Species
Abstract
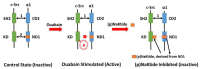
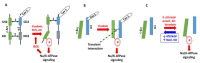
The signaling function of the Na/K-ATPase has been established for 20 years and is widely accepted in the field, with many excellent reports and reviews not cited here. Even though there is debate about the underlying mechanism, the signaling function is unquestioned. This short review looks back at the evolution of Na/K-ATPase signaling, from stimulation by cardiotonic steroids (also known as digitalis-like substances) as specific ligands to stimulation by reactive oxygen species (ROS) in general. The interplay of cardiotonic steroids and ROS in Na/K-ATPase signaling forms a positive-feedback oxidant amplification loop that has been implicated in some pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: Na/K-ATPase; ROS; Src. endocytosis; potassium; signaling; sodium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kometiani P., Li J., Gnudi L., Kahn B.B., Askari A., Xie Z. Multiple signal transduction pathways link Na+/K+-ATPase to growth-related genes in cardiac myocytes. The roles of Ras and mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:15249–15256. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.24.15249. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

