Heat Shock Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease: Role and Targeting
- PMID: 30200516
- PMCID: PMC6163571
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092603
Heat Shock Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease: Role and Targeting
Abstract
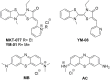
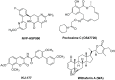
Among diseases whose cure is still far from being discovered, Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been recognized as a crucial medical and social problem. A major issue in AD research is represented by the complexity of involved biochemical pathways, including the nature of protein misfolding, which results in the production of toxic species. Considering the involvement of (mis)folding processes in AD aetiology, targeting molecular chaperones represents a promising therapeutic perspective. This review analyses the connection between AD and molecular chaperones, with particular attention toward the most important heat shock proteins (HSPs) as representative components of the human chaperome: Hsp60, Hsp70 and Hsp90. The role of these proteins in AD is highlighted from a biological point of view. Pharmacological targeting of such HSPs with inhibitors or regulators is also discussed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Hsp60; Hsp70; Hsp90; amyloid peptide; chaperones; heat shock proteins; protein Tau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

