PSEN1 p.Thr116Ile Variant in Two Korean Families with Young Onset Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30200536
- PMCID: PMC6164060
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092604
PSEN1 p.Thr116Ile Variant in Two Korean Families with Young Onset Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
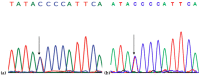
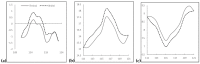
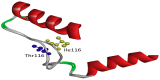
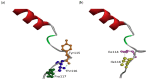
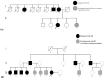
An in depth study of PSEN1 mutation p.Thr116Ile (c.335C>T) is presented from two Korean families with autosomal dominant inheritance. Clinical manifestation of our patients included memory loss, attention deficits, visuospatial dysfunction, agnosia, aphasia, apraxia, and personality changes, which occurred in their 30s. PSEN1 Thr116Ile was initially discovered in an Italian patient and two French families with early onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD) with similar age of onset. To verify the possible pathogenic mechanisms of mutation, in silico predictions and 3D modeling were performed. Structure predictions revealed significant aberrations in first hydrophilic loop (HL-I loop). The hydrophobic isoleucine could alter the loop orientation through increased hydrophobic contacts with the surrounding amino acids. Mutation could destroy a possible hydrogen bond between tyrosine 115 and threonine 116, which may affect the loop conformation. HL-I was confirmed as a conservative region of PSEN1, which may be critical in PSEN1 functions. An additional pathogenic mutation, PSEN1 Thr116Asn, was also found for the same residue, where the patient presented young onset AD (YOND). Other mutations in HL-I loop, such as Tyr115His and Glu120Asp, were described in patients with YOND, supporting the critical role of HL-I loop in PSEN1 activity.
Keywords: PSEN1 Thr116Ile mutation; familial; mutation; presenilin-1; young onset Alzheimer’s dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

