Serum Parathyroid Hormone, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 30200567
- PMCID: PMC6165184
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10091243
Serum Parathyroid Hormone, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
We conducted Mendelian randomization analyses to investigate the associations of serum parathyroid hormone (S-PTH) and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (S-25OHD) concentrations with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Five and seven single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with S-PTH and S-25OHD concentrations, respectively, were used as instrumental variables. Data for AD were acquired from the International Genomics of Alzheimer's Project (17,008 AD cases and 37,154 controls). Genetically higher S-PTH concentrations were not associated with AD (odds ratio per standard deviation increase in S-PTH = 1.11; 95% CI 0.97⁻1.26; p = 0.12). In contrast, all seven 25OHD-increasing alleles were inversely associated with AD and two of the associations were statistically significant (p < 0.05). The odds ratio of AD per genetically-predicted one standard deviation increase in S-25OHD was 0.86 (95% CI 0.78⁻0.94; p = 0.002). This study provides evidence that vitamin D may play a role in AD but found no significant association between S-PTH and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Mendelian randomization; parathyroid hormone; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
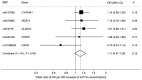
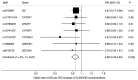
References
-
- Durk M.R., Han K., Chow E.C., Ahrens R., Henderson J.T., Fraser P.E., Pang K.S. 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces cerebral amyloid-beta accumulation and improves cognition in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2014;34:7091–7101. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2711-13.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

