Pharmacokinetics and Anti-Gastric Ulceration Activity of Oral Administration of Aceclofenac and Esomeprazole in Rats
- PMID: 30200587
- PMCID: PMC6160962
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030152
Pharmacokinetics and Anti-Gastric Ulceration Activity of Oral Administration of Aceclofenac and Esomeprazole in Rats
Abstract
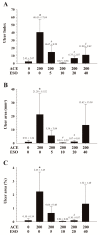
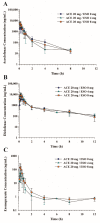
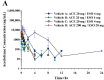
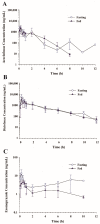
This study examined the effects of esomeprazole on aceclofenac pharmacokinetics and gastrointestinal complications in rats. Aceclofenac alone, or in combination with esomeprazole, was orally administered to male Sprague-Dawley rats. Plasma concentrations of aceclofenac, its major metabolite diclofenac, and esomeprazole were simultaneously determined by a novel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. Gastrointestinal damage was determined by measuring ulcer area and ulcer lesion index of the stomach. Oral administration of aceclofenac induced significant gastric ulceration, which was inhibited by esomeprazole administration. Following concurrent administration of aceclofenac and esomeprazole, overall pharmacokinetic profiles of aceclofenac and metabolic conversion to diclofenac were unaffected by esomeprazole. Aceclofenac metabolism and pharmacokinetics were not subject to significant food effects, whereas bioavailability of esomeprazole decreased in fed compared to fasting conditions. In contrast, the pharmacokinetics of aceclofenac and esomeprazole were significantly altered by different dosing vehicles. These results suggest that co-administration of esomeprazole with aceclofenac may reduce aceclofenac-induced gastrointestinal complications without significant pharmacokinetic interactions. The optimal combination and clinical significance of the benefits of the combination of aceclofenac and esomeprazole need to be further evaluated.
Keywords: aceclofenac; diclofenac; esomeprazole; gastric ulcer; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Y.-W.C., S.-M.C., K.-Y.N., and W.-H.K. are full-time employees of Korea United Pharm. Inc. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aceclofenac-Loaded Microspheres Prepared by Vesicular Ionotropic Gelation to Minimize Drug-induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(4):329-338. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220321111214. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35319360
-
Simultaneous analysis of acetylcarnitine, proline, hydroxyproline, citrulline, and arginine as potential plasma biomarkers to evaluate NSAIDs-induced gastric injury by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Feb 20;165:101-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.11.051. Epub 2018 Nov 24. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 30522064
-
Absolute bioavailability and metabolism of aceclofenac in rats.Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jan;38(1):68-72. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0350-4. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Arch Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 24633464
-
Pharmacokinetic studies with esomeprazole, the (S)-isomer of omeprazole.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001;40(6):411-26. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200140060-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001. PMID: 11475467 Review.
-
Aceclofenac: Species-Dependent Metabolism and Newer Paradigm Shift from Oral to Non-oral Delivery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(2):107-119. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160530152958. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27237333 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and in vitro Evaluation of Gastro-protective Aceclofenac-loaded Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery System.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jul 23;15:5217-5226. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S250242. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32801687 Free PMC article.
-
Development, In-Vitro Characterization and Preclinical Evaluation of Esomeprazole-Encapsulated Proniosomal Formulation for the Enhancement of Anti-Ulcer Activity.Molecules. 2022 Apr 25;27(9):2748. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092748. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batlle-Gualda E., Figueroa M., Ivorra J., Raber A. The efficacy and tolerability of aceclofenac in the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A multicenter controlled clinical trial. Aceclofenac indomethacin study group. J. Rheumatol. 1996;23:1200–1206. - PubMed
-
- Movilia P.G. Evaluation of the analgesic activity and tolerability of aceclofenac in the treatment of post-episiotomy pain. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1989;15:47–51. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

