Dme-Hsa Disease Database (DHDD): Conserved Human Disease-Related miRNA and Their Targeting Genes in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 30200613
- PMCID: PMC6163619
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092642
Dme-Hsa Disease Database (DHDD): Conserved Human Disease-Related miRNA and Their Targeting Genes in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
Abnormal expressions of microRNA (miRNA) can result in human diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. MiRNA mainly exert their biological functions via repressing the expression of their target genes. Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster) is an ideal model for studying the molecular mechanisms behind biological phenotypes, including human diseases. In this study, we collected human and D. melanogaster miRNA as well as known human disease-related genes. In total, we identified 136 human disease-related miRNA that are orthologous to 83 D. melanogaster miRNA by mapping "seed sequence", and 677 human disease-related genes that are orthologous to 734 D. melanogaster genes using the DRSC Integrative Ortholog Prediction Tool Furthermore, we revealed the target relationship between genes and miRNA using miRTarBase database and target prediction software, including miRanda and TargetScan. In addition, we visualized interaction networks and signalling pathways for these filtered miRNA and target genes. Finally, we compiled all the above data and information to generate a database designated DHDD This is the first comprehensive collection of human disease-related miRNA and their targeting genes conserved in a D. melanogaster database. The DHDD provides a resource for easily searching human disease-related miRNA and their disease-related target genes as well as their orthologs in D. melanogaster, and conveniently identifying the regulatory relationships among them in the form of a visual network.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; database; disease; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
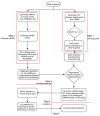
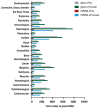
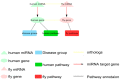

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

