Myosin Head Configurations in Resting and Contracting Murine Skeletal Muscle
- PMID: 30200618
- PMCID: PMC6165214
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092643
Myosin Head Configurations in Resting and Contracting Murine Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
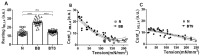
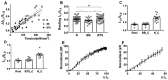
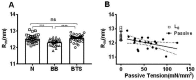
Transgenic mouse models have been important tools for studying the relationship of genotype to phenotype for human diseases, including those of skeletal muscle. We show that mouse skeletal muscle can produce high quality X-ray diffraction patterns establishing the mouse intact skeletal muscle X-ray preparation as a potentially powerful tool to test structural hypotheses in health and disease. A notable feature of the mouse model system is the presence of residual myosin layer line intensities in contracting mouse muscle patterns. This provides an additional tool, along with the I1,1/I1,0 intensity ratio, for estimating the proportions of active versus relaxed myosin heads under a given set of conditions that can be used to characterize a given physiological condition or mutant muscle type. We also show that analysis of the myosin layer line intensity distribution, including derivation of the myosin head radius, Rm, may be used to study the role of the super-relaxed state in myosin regulation. When the myosin inhibitor blebbistatin is used to inhibit force production, there is a shift towards a highly quasi-helically ordered configuration that is distinct from the normal resting state, indicating there are more than one helically ordered configuration for resting crossbridges.
Keywords: X-ray diffraction; actomyosin interaction; sarcomere structure; skeletal muscle; super-relaxed state.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




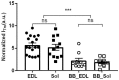
References
-
- Brunello E., Bianco P., Piazzesi G., Linari M., Reconditi M., Panine P., Narayanan T., Helsby W.I., Irving M., Lombardi V. Structural changes in the myosin filament and cross-bridges during active force development in single intact frog muscle fibres: Stiffness and X-ray diffraction measurements. J. Physiol. 2006;577:971–984. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.115394. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

