RBM4a-SRSF3-MAP4K4 Splicing Cascade Constitutes a Molecular Mechanism for Regulating Brown Adipogenesis
- PMID: 30200638
- PMCID: PMC6163301
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092646
RBM4a-SRSF3-MAP4K4 Splicing Cascade Constitutes a Molecular Mechanism for Regulating Brown Adipogenesis
Abstract
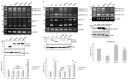
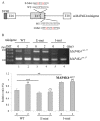
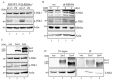
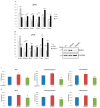
An increase in mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP4K4) reportedly attenuates insulin-mediated signaling which participates in the development of brown adipose tissues (BATs). Nevertheless, the effect of MAP4K4 on brown adipogenesis remains largely uncharacterized. In this study, results of a transcriptome analysis (also referred as RNA-sequencing) showed differential expressions of MAP4K4 or SRSF3 transcripts isolated from distinct stages of embryonic BATs. The discriminative splicing profiles of MAP4K4 or SRSF3 were noted as well in brown adipocytes (BAs) with RNA-binding motif protein 4-knockout (RBM4-/-) compared to the wild-type counterparts. Moreover, the relatively high expressions of authentic SRSF3 transcripts encoding the splicing factor functioned as a novel regulator toward MAP4K4 splicing during brown adipogenesis. The presence of alternatively spliced MAP4K4 variants exerted differential effects on the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) which was correlated with the differentiation or metabolic signature of BAs. Collectively, the RBM4-SRSF3-MAP4K4 splicing cascade constitutes a novel molecular mechanism in manipulating the development of BAs through related signaling pathways.
Keywords: MAP4K4; RBM4a; SRSF3; alternative splicing; brown adipocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RBM4-SRSF3-MAP4K4 splicing cascade modulates the metastatic signature of colorectal cancer cell.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Feb;1865(2):259-272. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29138007
-
RBM4-Nova1-SRSF6 splicing cascade modulates the development of brown adipocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Nov;1859(11):1368-1379. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27535496
-
RBM4a modulates the impact of PRDM16 on development of brown adipocytes through an alternative splicing mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Nov;1865(11 Pt A):1515-1525. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30327195
-
Map4k4 Signaling Nodes in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul;27(7):484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 May 6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27160798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic SRSF3 in health and diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;19(10):3057-3076. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83368. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory roles and mechanisms of alternative RNA splicing in adipogenesis and human metabolic health.Cell Biosci. 2021 Apr 1;11(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00581-w. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33795017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAP4K4/JNK Signaling Pathway Stimulates Proliferation and Suppresses Apoptosis of Human Spermatogonial Stem Cells and Lower Level of MAP4K4 Is Associated with Male Infertility.Cells. 2022 Nov 28;11(23):3807. doi: 10.3390/cells11233807. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497065 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals regulation of adipogenesis via long non-coding RNA, alternative splicing, and alternative polyadenylation.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 23;14(1):16964. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67648-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39043790 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA Ctcflos orchestrates transcription and alternative splicing in thermogenic adipogenesis.EMBO Rep. 2021 Jul 5;22(7):e51289. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051289. Epub 2021 May 31. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34056831 Free PMC article.
-
SRSF3 and hnRNP A1-mediated m6A-modified circCDK14 regulates intramuscular fat deposition by acting as miR-4492-z sponge.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Mar 4;30(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00699-6. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40038607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim S.P., Frey J.L., Li Z., Kushwaha P., Zoch M.L., Tomlinson R.E., Da H., Aja S., Noh H.L.J., Kim K., et al. Sclerostin influences body composition by regulating catabolic and anabolic metabolism in adipocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E11238–E11247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707876115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hung C., Bronec C., Napoli E., Graham J., Stanhope K.L., Marsilio L., Giron M.C., Havel P.J., Giulivi C. Adipose depot-specific effects of ileal interposition surgery in UCD-T2D rats: Unexpected implications for obesity and diabetes. Biochem. J. 2018;475:649–662. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170899. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xiong Y., Yue F., Jia Z., Gao Y., Jin W., Hu K., Zhang Y., Zhu D., Yang G., Kuang S. A novel brown adipocyte-enriched long non-coding RNA that is required for brown adipocyte differentiation and sufficient to drive thermogenic gene program in white adipocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2018;1863:409–419. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.01.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

