Single-molecule long-read transcriptome profiling of Platysternon megacephalum mitochondrial genome with gene rearrangement and control region duplication
- PMID: 30200821
- PMCID: PMC6284601
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1521212
Single-molecule long-read transcriptome profiling of Platysternon megacephalum mitochondrial genome with gene rearrangement and control region duplication
Abstract
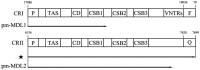
Platysternon megacephalum is the sole living representative of the poorly studied turtle lineage Platysternidae. Their mitochondrial genome has been subject to gene rearrangement and control region duplication, resulting in a unique mitochondrial gene order in vertebrates. In this study, we sequenced the first full-length turtle (P. megacephalum) liver transcriptome using single-molecule real-time sequencing to study the transcriptional mechanisms of its mitochondrial genome. ND5 and ND6 anti-sense (ND6AS) forms a single transcript with the same expression in the human mitochondrial genome, but here we demonstrated differential expression of the rearranged ND5 and ND6AS genes in P. megacephalum. And some polycistronic transcripts were also reported in this study. Notably, we detected some novel long non-coding RNAs with alternative polyadenylation from the duplicated control region, and a novel ND6AS transcript composed of a long non-coding sequence, ND6AS, and tRNA-GluAS. These results provide the first description of a mtDNA transcriptome with gene rearrangement and control region duplication. These findings further our understanding of the fundamental concepts of mitochondrial gene transcription and RNA processing, and provide a new insight into the mechanism of transcription regulation of the mitochondrial genome.
Keywords: CR duplication; Platysternon megacephalum; full-length transcriptome; gene rearrangement; mtDNA.
Figures


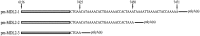

Similar articles
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of Chinese big-headed turtle, Platysternon megacephalum, with a novel gene organization in vertebrate mtDNA.Gene. 2006 Sep 15;380(1):14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.04.001. Epub 2006 Apr 28. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16842936
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the enigmatic bigheaded turtle (Platysternon): description of unusual genomic features and the reconciliation of phylogenetic hypotheses based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA.BMC Evol Biol. 2006 Feb 7;6:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-6-11. BMC Evol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16464263 Free PMC article.
-
Taxonomic revision of the critically endangered big-headed turtles (Reptilia: Testudines: Platysternidae Gray, 1869), with description of a new species.Zool Res. 2025 Sep 18;46(5):1047-1058. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2025.197. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 40923303
-
Draft genome of the big-headed turtle Platysternon megacephalum.Sci Data. 2019 May 16;6(1):60. doi: 10.1038/s41597-019-0067-9. Sci Data. 2019. PMID: 31097710 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination and evolution of duplicate control regions in the mitochondrial genome of the Asian big-headed turtle, Platysternon megacephalum.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 18;8(12):e82854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082854. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24367563 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Guidelines for mitochondrial RNA analysis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jun 26;35(3):102262. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102262. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39091381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome sequencing and comparative analysis of adult ovary and testis identify potential gonadal maintenance-related genes in Mauremys reevesii with temperature-dependent sex determination.PeerJ. 2019 Mar 8;7:e6557. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6557. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30867990 Free PMC article.
-
Using Pan RNA-Seq Analysis to Reveal the Ubiquitous Existence of 5' and 3' End Small RNAs.Front Genet. 2019 Feb 14;10:105. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00105. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30838030 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Adult Testis and Ovary MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Reeves' Pond Turtles (Mauremys reevesii) With Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination.Front Genet. 2020 Mar 2;11:133. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00133. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32194623 Free PMC article.
-
Full-length transcriptome sequences of Agropyron cristatum facilitate the prediction of putative genes for thousand-grain weight in a wheat-A. cristatum translocation line.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 27;20(1):1025. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6416-4. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31881839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clayton DA. Transcription and replication of animal mitochondrial DNAs Int Rev Cytol. 1992;141:217–232. - PubMed
-
- Peng QL, Nie LW, Pu YG. Complete mitochondrial genome of Chinese big-headed turtle, Platysternon megacephalum, with a novel gene organization in vertebrate mtDNA. Gene. 2006;380:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Shao R, Barker SC, Mitani H, et al. Evolution of duplicate control regions in the mitochondrial genomes of metazoa: a case study with australasian ixodes ticks. Mol Biol Evol. 2005;22:620–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
