Malignancy rates of B3-lesions in breast magnetic resonance imaging - do all lesions have to be excised?
- PMID: 30200900
- PMCID: PMC6131767
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-018-0271-7
Malignancy rates of B3-lesions in breast magnetic resonance imaging - do all lesions have to be excised?
Abstract
Background: Approximately 10% of all MRI-guided vacuum-assisted breast biopsies (MR-VAB) are histologically classified as B3 lesions. In most of these cases surgical excision is recommended. The aim of our study was to evaluate the malignancy rates of different B3 lesions which are visible on MRI to allow a lesion-adapted recommendation of further procedure.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of 572 consecutive MR-VAB was performed. Inclusion criteria were a representative (=successful) MR-VAB, histologic diagnosis of a B3 lesion and either the existence of a definite histology after surgical excision or proof of stability or regression of the lesion on follow-up MRI. Malignancy rates were evaluated for different histologies of B3 lesions. Lesion size and lesion morphology (mass/non-mass enhancement) on MRI were correlated with malignancy.
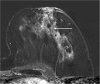
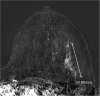
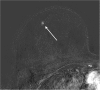
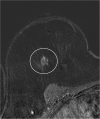
Results: Of all MR-VAB 43 lesions fulfilled the inclusion criteria. The malignancy rate of those B3 lesions was 23.3% (10/43). The highest malignancy rate was found in atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) lesions (50.0%; 4/8), 33.3% (2/6) in flat epithelial atypia (FEA), 28.6% (2/7) in lobular intraepithelial neoplasia (LIN) and 12.5% (2/16) in papillary lesions (PL). All 6 complex sclerosing lesions were benign. Mass findings were significantly more frequently malignant (31.3%, 10/32; p < 0.05) than non-mass findings (0/11). Small lesions measuring 5-10 mm were most often malignant (35.0%; 7/20). All large lesions (> 20 mm) were not malignant (0/10). Intermediate sized lesions (11-20 mm) turned out to be malignant in 23.1% (3/13).
Conclusions: The malignancy rate of B3 lesions which were diagnosed after MR-VAB was 23.3%. ADH, FEA and LIN showed considerable malignancy rates (50%, 33% and 29%) and should therefore undergo surgical excision. None of the cases, which were diagnosed as radial scars, non-mass enhancement or larger lesions (> 20 mm) were malignant. Here, a follow-up MRI seems to be advisable to avoid unnecessary operations.
Trial registration: Retrospective study design, waived by the IRB.
Keywords: B3 lesions; Breast MRI; MRI-guided breast biopsy; Vacuum-assisted biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
For this retrospective study written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Tuebingen (No. 372/2017BO2).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Morris EA, Comstock CE, Lee CH, et al. ACR BI-RADS® Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston: American College of Radiology; 2013. ACR BI-RADS® Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
-
- Wells CAAI, Apostolikas N, Bellocq JP. Quality assurance guidelines for pathology. In: Perry NMBM, de Wolf C, editors. EC working group on breast screening pathology: Quality assurance guidelines for pathology in mammography screening – open biopsy and resection specimens European guidelines for quality assurance in mammography screening. 4. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the Eropean Communities; 2006. pp. 219–256.
-
- Saladin C, Haueisen H, Kampmann G, Oehlschlegel C, Seifert B, Rageth L, et al. Lesions with unclear malignant potential (B3) after minimally invasive breast biopsy: evaluation of vacuum biopsies performed in Switzerland and recommended further management. Acta Radiol. 2016;57:815–821. doi: 10.1177/0284185115610931. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

