The Terry Fox Research Institute Canadian Prostate Cancer Biomarker Network: an analysis of a pan-Canadian multi-center cohort for biomarker validation
- PMID: 30200929
- PMCID: PMC6131811
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-018-0392-x
The Terry Fox Research Institute Canadian Prostate Cancer Biomarker Network: an analysis of a pan-Canadian multi-center cohort for biomarker validation
Abstract
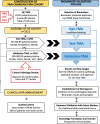
Background: Refinement of parameters defining prostate cancer (PC) prognosis are urgently needed to identify patients with indolent versus aggressive disease. The Canadian Prostate Cancer Biomaker Network (CPCBN) consists of researchers from four Canadian provinces to create a validation cohort to address issues dealing with PC diagnosis and management.
Methods: A total of 1512 radical prostatectomy (RP) specimens from five different biorepositories affiliated with teaching hospitals were selected to constitute the cohort. Tumoral and adjacent benign tissues were arrayed on tissue microarrays (TMAs). A patient clinical database was developed and includes data on diagnosis, treatment and clinical outcome.
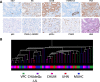
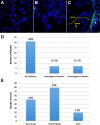
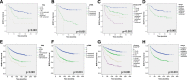
Results: Mean age at diagnosis of patients in the cohort was 61 years. Of these patients, 31% had a low grade (≤6) Gleason score (GS), 55% had GS 7 (40% of 3 + 4 and 15% of 4 + 3) and 14% had high GS (≥8) PC. The median follow-up of the cohort was 113 months. A total of 34% had a biochemical relapse, 4% developed bone metastasis and 3% of patients died from PC while 9% died of other causes. Pathological review of the TMAs confirmed the presence of tumor and benign tissue cores for > 94% of patients. Immunohistochemistry and FISH analyses, performed on a small set of specimens, showed high quality results and no biorepository-specific bias.
Conclusions: The CPCBN RP cohort is representative of real world PC disease observed in the Canadian population. The frequency of biochemical relapse and bone metastasis as events allows for a precise assessment of the prognostic value of biomarkers. This resource is available, in a step-wise manner, for researchers who intend to validate prognostic biomarkers in PC. Combining multiple biomarkers with clinical and pathologic parameters that are predictive of outcome will aid in clinical decision-making for patients treated for PC.
Keywords: Biomarker validation; Immunohistochemistry; Patient prognosis; Prostate cancer; Tissue microarray.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Research ethics approval was obtained from each of the participating sites: the Centre de recherche du Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CRCHUM), CHU de Québec-Université Laval (CHUdeQ-UL), McGill University Health Centre (MUHC), Vancouver Prostate Centre (VPC), and University Health Network (UHN). All patients signed an informed consent to participate within one of the biobanks and agreed to the use of their specimens and data for research purposes.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Huber F, Montani M, Sulser T, Jaggi R, Wild P, Moch H, et al. Comprehensive validation of published immunohistochemical prognostic biomarkers of prostate cancer -what has gone wrong? A blueprint for the way forward in biomarker studies. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(1):140–148. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.588. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

