The development of the error-related negativity in large sample of adolescent females: Associations with anxiety symptoms
- PMID: 30201401
- PMCID: PMC6279523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2018.09.003
The development of the error-related negativity in large sample of adolescent females: Associations with anxiety symptoms
Abstract
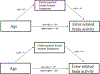
Anxiety is the most common form of psychopathology and tends to begin early in the course of development. Given this, there is great interest in identifying developmental changes in neural systems that may delineate healthy versus anxious trajectories. A substantial amount of work has focused on the error-related negativity as a neural marker of anxiety. The ERN is a negative deflection in the event-related potential that occurs when individuals make mistakes and is increased in anxious individuals. A separate body of work has focused on normative developmental changes in the ERN - demonstrating an age-related increase in the ERN that occurs across childhood and adolescence. In the current study, we examine the ERN in relation to specific phenotypic expressions of anxiety during a core risk period in a sample of females (N = 220) ranging from 8 to 14 years old. Results from the current study suggest that error-related brain activity is related to both parent and child report of social anxiety symptoms, even when controlling for all other symptom scales. Additionally, mediation models suggest that the normative developmental increase observed in the ERN is partially mediated by increases in social anxiety symptoms. The current results are novel insofar as they identify a specific phenotypic expression of anxiety that underlies developmental increases in this neural biomarker.
Keywords: Adolescents; Anxiety; Biomarker; Children; Development; Error-related negativity (ERN); Event-related potentials (ERPs).
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
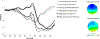
References
-
- Ball TM, Stein MB, & Paulus MP (2014). Toward the application of functional neuroimaging to individualized treatment for anxiety and depression. Depression and anxiety, 31(11), 920–933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

