Impaired brain glymphatic flow in experimental hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 30201461
- PMCID: PMC7613052
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.021
Impaired brain glymphatic flow in experimental hepatic encephalopathy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Impaired brain glymphatic flow in experimental hepatic encephalopathy" [J Hepatol 69 (2019) 40-49].J Hepatol. 2019 Mar;70(3):582. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.012. Epub 2019 Jan 5. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30616987 No abstract available.
Abstract
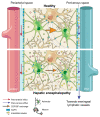
Background & aims: Neuronal function is exquisitely sensitive to alterations in the extracellular environment. In patients with hepatic encephalopathy (HE), accumulation of metabolic waste products and noxious substances in the interstitial fluid of the brain is thought to result from liver disease and may contribute to neuronal dysfunction and cognitive impairment. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that the accumulation of these substances, such as bile acids, may result from reduced clearance from the brain.
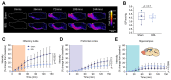
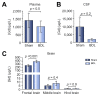
Methods: In a rat model of chronic liver disease with minimal HE (the bile duct ligation [BDL] model), we used emerging dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and mass-spectroscopy techniques to assess the efficacy of the glymphatic system, which facilitates clearance of solutes from the brain. Immunofluorescence of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) and behavioural experiments were also performed.
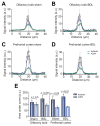
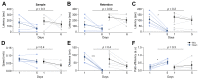
Results: We identified discrete brain regions (olfactory bulb, prefrontal cortex and hippocampus) of altered glymphatic clearance in BDL rats, which aligned with cognitive/behavioural deficits. Reduced AQP4 expression was observed in the olfactory bulb and prefrontal cortex in HE, which could contribute to the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the impairment in glymphatic function in BDL rats.
Conclusions: This study provides the first experimental evidence of impaired glymphatic flow in HE, potentially mediated by decreased AQP4 expression in the affected regions.
Lay summary: The 'glymphatic system' is a newly discovered brain-wide pathway that facilitates clearance of various substances that accumulate in the brain due to its activity. This study evaluated whether the function of this system is altered in a model of brain dysfunction that occurs in cirrhosis. For the first time, we identified that the clearance of substances from the brain in cirrhosis is reduced because this clearance system is defective. This study proposes a new mechanism of brain dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis and provides new targets for therapy.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; Glymphatic system; Hepatic encephalopathy; MRI; Mass spectrometry.
Copyright © 2018 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Rajiv Jalan has research collaborations with Yaqrit and Takeda. Rajiv Jalan is the inventor of OPA, which has been patented by UCL and licensed to Mallinckrodt Pharma. He is also the founder of Yaqrit limited, a spin out company from University College London. All other authors report no conflict of interest.
Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures


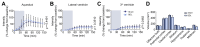

Comment in
-
Hepatic encephalopathy: Another brick in the wall.J Hepatol. 2019 Jan;70(1):8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Nov 7. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30414737 No abstract available.
-
A hydrodynamic hypothesis for the pathogenesis of glymphatic system impairment in hepatic encephalopathy.J Hepatol. 2019 Jul;71(1):228-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 May 3. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31060841 No abstract available.
References
-
- Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(147):147ra11. doi: 10.1126/sci-translmed.3003748. [published Online First: 2012/08/17] - DOI - PMC - PubMed

