Signaling through non-membrane nuclear phosphoinositide binding proteins in human health and disease
- PMID: 30201631
- PMCID: PMC6358298
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R088518
Signaling through non-membrane nuclear phosphoinositide binding proteins in human health and disease
Abstract
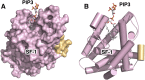
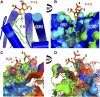
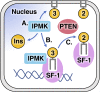
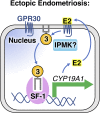
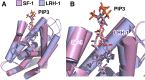
Phosphoinositide membrane signaling is critical for normal physiology, playing well-known roles in diverse human pathologies. The basic mechanisms governing phosphoinositide signaling within the nucleus, however, have remained deeply enigmatic owing to their presence outside the nuclear membranes. Over 40% of nuclear phosphoinositides can exist in this non-membrane state, held soluble in the nucleoplasm by nuclear proteins that remain largely unidentified. Recently, two nuclear proteins responsible for solubilizing phosphoinositides were identified, steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1; NR5A1) and liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1; NR5A2), along with two enzymes that directly remodel these phosphoinositide/protein complexes, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN; MMAC) and inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK; ipk2). These new footholds now permit the assignment of physiological functions for nuclear phosphoinositides in human diseases, such as endometriosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/steatohepatitis, glioblastoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The unique nature of nuclear phosphoinositide signaling affords extraordinary clinical opportunities for new biomarkers, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thus, phosphoinositide biology within the nucleus may represent the next generation of low-hanging fruit for new drugs, not unlike what has occurred for membrane phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase drug development. This review connects recent basic science discoveries in nuclear phosphoinositide signaling to clinical pathologies, with the hope of inspiring development of new therapies.
Keywords: diabetes; endometriosis; glioblastoma; hepatocellular carcinoma; inositol phosphate multikinase; nuclear lipid signaling; phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5) triphosphate.
Copyright © 2019 Bryant and Blind.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has an actual or perceived conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural analyses of inositol phosphate second messengers bound to signaling effector proteins.Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Jan;75:100667. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.100667. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 31648945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SF-1 Induces Nuclear PIP2.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 12;13(10):1509. doi: 10.3390/biom13101509. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892191 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Liver Receptor Homolog-1 (NR5A2) with PIP3 hormone bound in the ligand binding pocket.J Struct Biol. 2015 Dec;192(3):342-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.09.012. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 26416531 Free PMC article.
-
The Orphan Nuclear Receptors Steroidogenic Factor-1 and Liver Receptor Homolog-1: Structure, Regulation, and Essential Roles in Mammalian Reproduction.Physiol Rev. 2019 Apr 1;99(2):1249-1279. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2018. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30810078 Review.
-
Pharmacology of phosphoinositides, regulators of multiple cellular functions.Curr Pharm Des. 2001 Apr;7(6):475-507. doi: 10.2174/1381612013397906. Curr Pharm Des. 2001. PMID: 11281854 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippo and PI5P4K signaling intersect to control the transcriptional activation of YAP.Sci Signal. 2024 May 28;17(838):eado6266. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.ado6266. Epub 2024 May 28. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 38805583 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma membrane and nuclear phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate signalling in cancer.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Feb 6;24(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02452-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 39915829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New High-Throughput Screen Discovers Novel Ligands of Full-Length Nuclear Receptor LRH-1.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 May 19;18(5):1101-1114. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00805. Epub 2023 Apr 19. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37074920 Free PMC article.
-
The oily nucleus- role of phospholipids in genome biology: membrane-directed roles and signaling in the nucleoplasm.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jul 25;82(1):286. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05825-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40711532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Modulating Phosphoinositide Profiles as a Roadmap for Treatment in Acute Myeloid Leukemia".Front Oncol. 2021 May 24;11:678824. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.678824. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34109125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Persidis A. 1998. Signal transduction as a drug-discovery platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 16: 1082–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

