Histophilus somni Survives in Bovine Macrophages by Interfering with Phagosome-Lysosome Fusion but Requires IbpA for Optimal Serum Resistance
- PMID: 30201700
- PMCID: PMC6246896
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00365-18
Histophilus somni Survives in Bovine Macrophages by Interfering with Phagosome-Lysosome Fusion but Requires IbpA for Optimal Serum Resistance
Abstract
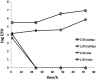
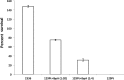
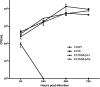
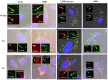
Histophilus somni is capable of intracellular survival within professional phagocytic cells, but the mechanism of survival is not understood. The Fic motif within the direct repeat (DR1)/DR2 domains of the IbpA fibrillary network protein of H. somni is cytotoxic to epithelial and phagocytic cells, which may interfere with the bactericidal activity of these cells. To determine the contribution of IbpA and Fic to resistance to host defenses, H. somni strains and mutants that lacked all or a region of ibpA (including the DR1/DR2 regions) were tested for survival in bovine monocytic cells and for serum susceptibility. An H. somni mutant lacking IbpA, but not the DR1/DR2 region within ibpA, was more susceptible to killing by antiserum than the parent, indicating that the entire protein was associated with serum resistance. H. somni strains expressing IbpA replicated in bovine monocytes for at least 72 h and were toxic for these cells. Virulent strain 2336 mutants lacking the entire ibpA gene or both DR1 and DR2 were not toxic to the monocytes but still survived within the monocytes for at least 72 h. Monitoring of intracellular trafficking of H. somni with monoclonal antibodies to phagosomal markers indicated that the early phagosomal marker early endosome antigen 1 colocalized with all isolates tested, but only strains that could survive intracellularly did not colocalize with the late lysosomal marker lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 and prevented the acidification of phagosomes. These results indicated that virulent isolates of H. somni were capable of surviving within phagocytic cells through interference in phagosome-lysosome maturation. Therefore, H. somni may be considered a permissive intracellular pathogen.
Keywords: Fic motif; Histophilus somni; IbpA; bactericidal activity; intracellular bacteria; monocytes; phagocytosis.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Histophilus somni IbpA DR2/Fic in virulence and immunoprotection at the natural host alveolar epithelial barrier.Infect Immun. 2010 May;78(5):1850-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01277-09. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20176790 Free PMC article.
-
Histophilus somni IbpA Fic cytotoxin is conserved in disease strains and most carrier strains from cattle, sheep and bison.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Apr 21;149(1-2):177-85. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.10.012. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21112704
-
IbpA DR2 subunit immunization protects calves against Histophilus somni pneumonia.Vaccine. 2011 Jun 24;29(29-30):4805-12. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.04.075. Epub 2011 May 8. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21557979
-
Host Immune Response to Histophilus somni.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;396:109-29. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_5012. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26728062 Review.
-
Histophilus somni Surface Proteins.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;396:89-107. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_5011. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26728061 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Hfq to gene regulation and virulence in Histophilus somni.Infect Immun. 2024 Mar 12;92(3):e0003824. doi: 10.1128/iai.00038-24. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38391206 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Network Analysis to Identify Key Modules and Potential Hub Genes Involved in Bovine Respiratory Disease: A Systems Biology Approach.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 18;12:753839. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.753839. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34733317 Free PMC article.
-
Annotation of Functions of Sequences of Concern and Its Relevance to the New Biosecurity Regulatory Framework in the United States.Appl Biosaf. 2024 Sep 18;29(3):142-149. doi: 10.1089/apb.2023.0030. eCollection 2024 Sep. Appl Biosaf. 2024. PMID: 39372509 Free PMC article.
-
Categorizing Sequences of Concern by Function To Better Assess Mechanisms of Microbial Pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2022 May 19;90(5):e0033421. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00334-21. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 34780277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of Histophilus somni strains isolated in Russia.Vet World. 2023 Feb;16(2):272-280. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2023.272-280. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Vet World. 2023. PMID: 37042002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sandal I, Corbeil L, Inzana T. 2010. Haemophilus, p 387–409. In Gyles CL, Prescott JF, Songer G, Thoen CO (ed), Pathogenesis of bacterial infections in animals, 4th ed Blackwell Publishing, Ames, IA.
-
- Challacombe JF, Duncan AJ, Brettin TS, Bruce D, Chertkov O, Detter JC, Han CS, Misra M, Richardson P, Tapia R, Thayer N, Xie G, Inzana TJ. 2007. Complete genome sequence of Haemophilus somnus (Histophilus somni) strain 129Pt and comparison to Haemophilus ducreyi 35000HP and Haemophilus influenzae Rd. J Bacteriol 189:1890–1898. doi:10.1128/JB.01422-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stephens LR, Little PB, Humphrey JD, Wilkie BN, Barnum DA. 1982. Vaccination of cattle against experimentally induced thromboembolic meningoencephalitis with a Haemophilus somnus bacterin. Am J Vet Res 43:1339–1342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

