Vagus Nerve Stimulation at the Interface of Brain-Gut Interactions
- PMID: 30201788
- PMCID: PMC6671930
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034199
Vagus Nerve Stimulation at the Interface of Brain-Gut Interactions
Abstract
The vagus nerve, a key component of the cross-communication between the gut and the brain, is a major element of homeostasis sensing the "milieu intérieur" and boosting the nervous and endocrine responses to maintain the gastrointestinal health status. This nerve has anti-inflammatory properties regulating the gut through the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the release of cortisol and through a vagovagal reflex, which has an anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) effect called the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Stimulating this nerve is an interesting tool as a nondrug therapy for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases in which brain-gut communication is dysfunctional, such as inflammatory bowel disorders and others. This review presents the rationale of vagal gastrointestinal physiology and diseases and the most recent advances in vagus nerve stimulation. It also highlights the main issues to be addressed in the future to improve this bioelectronic therapy for gastrointestinal disorders.
Copyright © 2019 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

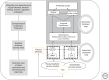

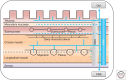

References
-
- Agostini A, Ballotta D, Righi S, Moretti M, Bertani A, Scarcelli A, Sartini A, Ercolani M, Nichelli P, Campieri M, et al. 2017. Stress and brain functional changes in patients with Crohn’s disease: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 29: 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Barquist E, Bonaz B, Martinez V, Rivier J, Zinner MJ, Tache Y. 1996. Neuronal pathways involved in abdominal surgery-induced gastric ileus in rats. Am J Physiol 270: R888–R894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
